4.6 — Sequential Bayesian Games
ECON 316 • Game Theory • Fall 2021
Ryan Safner
Assistant Professor of Economics
safner@hood.edu
ryansafner/gameF21
gameF21.classes.ryansafner.com
Sequential Bayesian Games
Equilibrium in Sequential Bayesian Games
We looked at a simultaneous game of incomplete information
Now let's look at some common models of sequential games with incomplete information, and some famous applications
Again, typically assume that Player 2 has private information about their “type,” that Player 1 does not know

Equilibrium in Sequential Bayesian Games
We needed Bayes’ Rule because we will use it to describe how rational players update their beliefs (about others’ type) when presented with new evidence (i.e., the other player makes a move)
Players share common (prior) belief about likelihood of encountering a player-type (p)
Informed player with private information (their type) will make a move, uninformed player will update their belief about that player’s type

Our Previous Bayesian Example as a Signalling Game
Consider our previous game in sequential form
A signalling game where Colin moves first
Rowena observes Colin's move (Cooperate or Defect), but does not know which type Colin is (and thus, the consequences of her own move)
We could again find what conditions lead to valid pooling equilibria and separating equilibria
- But I'd rather focus on applications of these famous models
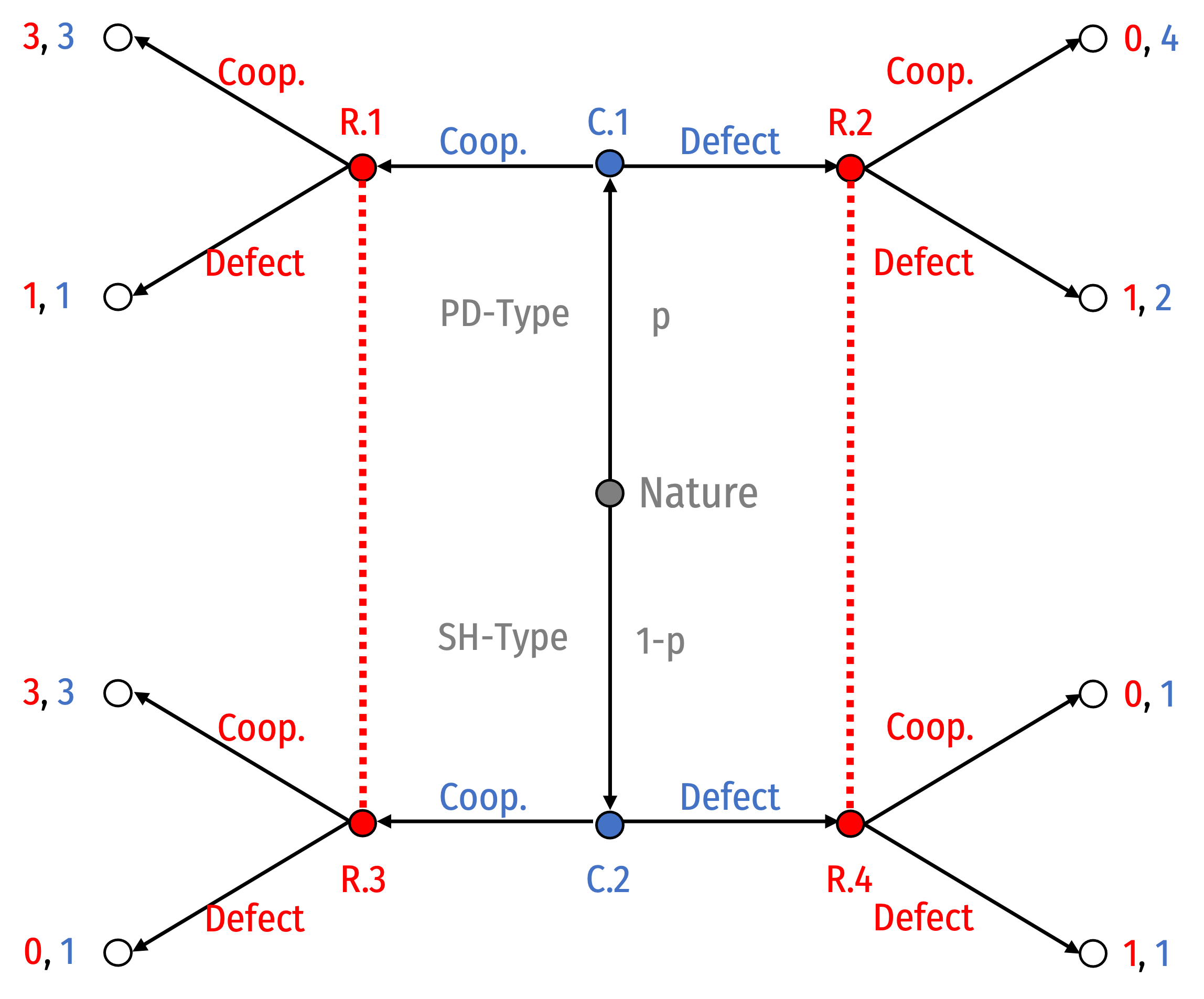
Our Previous Bayesian Example as a Signalling Game
Essentially, Colin makes a move, either Cooperate or Defect
Rowena’s prior beliefs about Colin’s type (p) get updated based on Colin’s move
Then Rowena must decide how to respond, given her (updated) posterior belief about Colin’s type

Perfect Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (PBNE)
- A possible solution for a sequential game with incomplete (asymmetric) information is known as an assessment which has two parts:
A behavioral strategy profile: complete plan of action for each player about how to play at each information set
A belief system: probability distribution over nodes in each information set
- estimate how likely a player is a particular type, given their action

Perfect Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (PBNE)
- An assessment is a Perfect Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (PBNE) if it fits both conditions:
- Sequentially rational — i.e. credible & survives backwards induction
- at each information set, strategies are optimal given beliefs
- It is consistent with Bayes’ Rule
- beliefs are updated by Bayes' Rule wherever possible
“given the other player has played X, how likely are they type I?”
- The analog of subgame perfect Nash equilibrium, but with incomplete information

Signaling vs. Screening Games
Used to explore the economic problem of adverse selection: informed players exploit uninformed players
- Again, one player has private information (their type), the other doesn’t know
Let Player 1 be the “uninformed player”
Player 2 be the “informed player” with private information about their type

Signaling vs. Screening Games
- Two types of sequential games with adverse selection:
Screening games: uninformed player moves first
- Will try to determine what type the other player is
- Offer options where informed players can self-select and reveal their type
Signaling games: informed player moves first
- Will try to signal their type to uninformed player
- But “bad”-types also want to signal they are “good”-types!

Screening Games
A Biblical Example of Screening
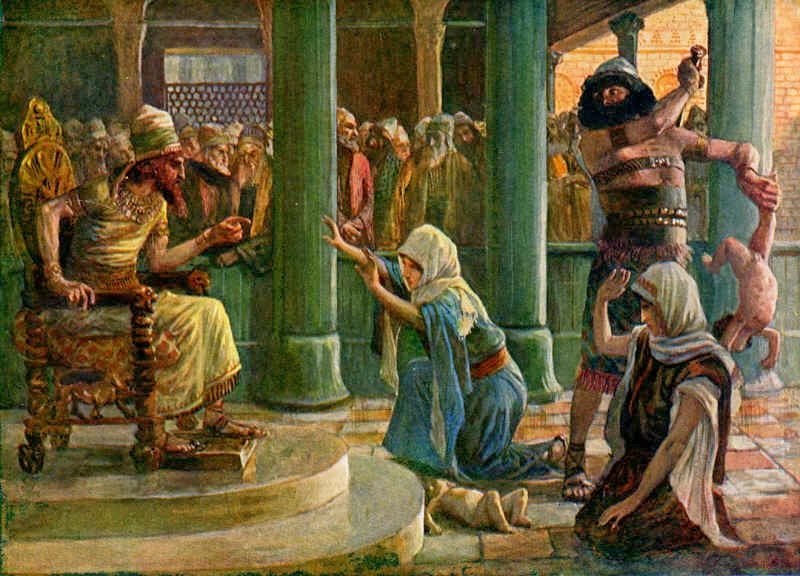

One day two women came to King Solomon, and one of them said:
Your Majesty, this woman and I live in the same house. Not long ago my baby was born at home, and three days later her baby was born. Nobody else was there with us.
One night while we were all asleep, she rolled over on her baby, and he died. Then while I was still asleep, she got up and took my son out of my bed. She put him in her bed, then she put her dead baby next to me.
In the morning when I got up to feed my son, I saw that he was dead. But when I looked at him in the light, I knew he wasn’t my son.
"No!" the other woman shouted. "He was your son. My baby is alive!"
"The dead baby is yours," the first woman yelled. "Mine is alive!"
A Biblical Example of Screening

They argued back and forth in front of Solomon, until finally he said, "Both of you say this live baby is yours. Someone bring me a sword."
A sword was brought, and Solomon ordered, "Cut the baby in half! That way each of you can have part of him."
"Please don’t kill my son," the baby’s mother screamed. "Your Majesty, I love him very much, but give him to her. Just don’t kill him."
The other woman shouted, "Go ahead and cut him in half. Then neither of us will have the baby."
Solomon said, "Don’t kill the baby." Then he pointed to the first woman, "She is his real mother. Give the baby to her."
A Modern Example of Screening


Screening to Mitigate Adverse Selection


Price Discrimination to Mitigate Adverse Selection
2nd-degree price discrimination: seller doesn’t know what type of buyer they are selling to (low/elastic vs. high/inelastic willingness to pay)
If it knew, it could offer different customers different prices based on some observable characteristic (1st- and 3rd-degree PD)

Price Discrimination to Mitigate Adverse Selection
- Common example: block pricing & quantity discounts
- Firm offers different prices for different quantities of the good
- Charge customers that buy larger quantities a lower price per unit
- Must be incentive—compatible: low-volume customers must want to pay the higher price for fewer than the discounted price for more
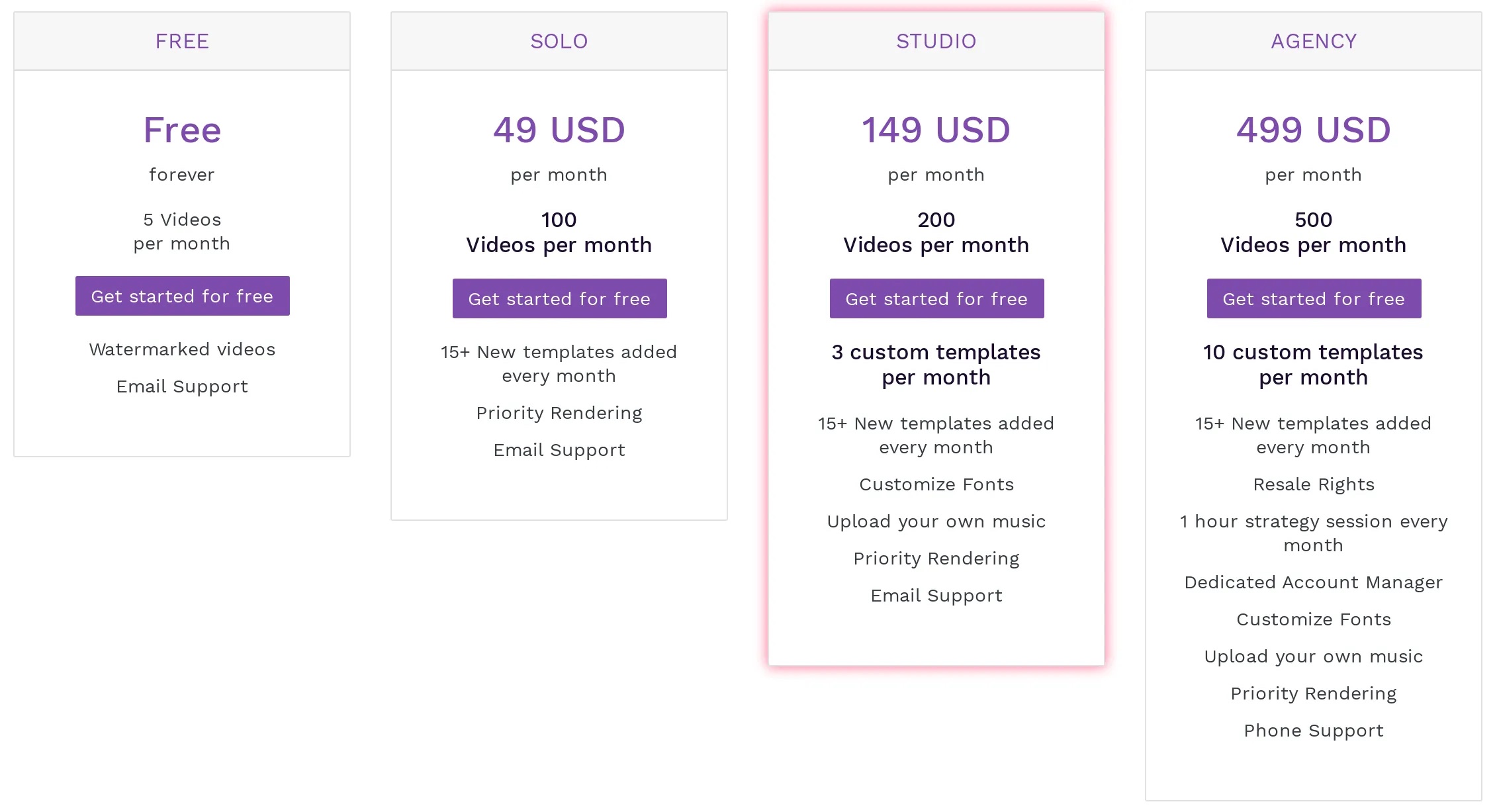
Price Discrimination to Mitigate Adverse Selection
- Common example: versioning
- Firm offers different prices for different qualities of the good
- Charge customers that higher price for higher quality
- Must be incentive—compatible: high-WTP/inelastic customers must want to pay the higher price instead of the discounted price
“What the company is trying to do is to prevent the passengers who can pay the second class fare from traveling third class; It hits the poor, not because it wants to hurt them, but to frighten the rich.” — Jules Dupuit, 1849
Signaling Example I: Akerlof (1970) — The Market for Lemons
The Market for Lemons
Consider the used car market
Two types of used cars
- “Lemon”: low-quality car
- “Peach”: high-quality car
Suppose you, the buyer value a peach at H and a lemon at L dollars
You cannot tell a good car from a bad one, but believe some fraction q of cars are Peaches

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
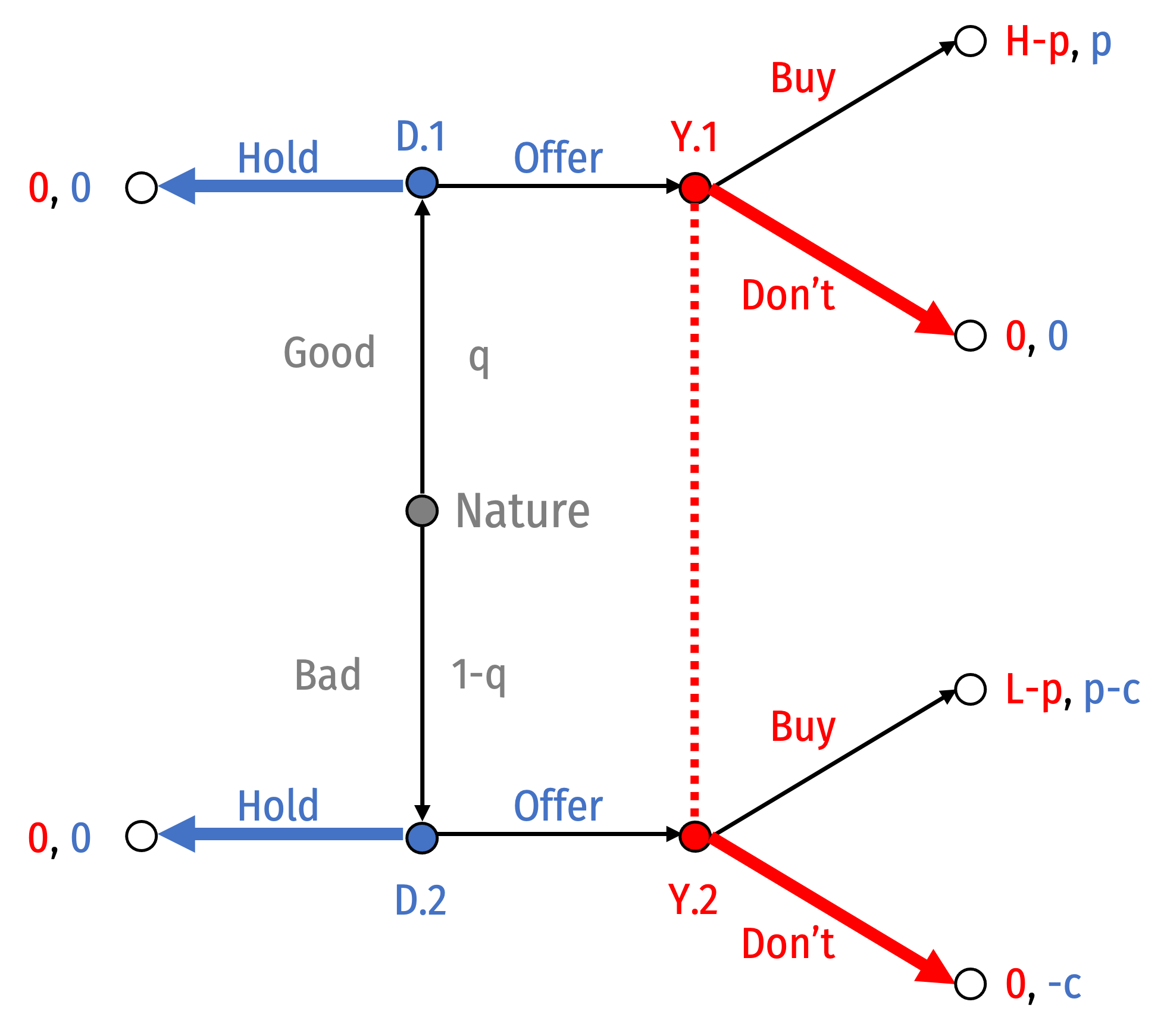
The Market for Lemons
Suppose a particular car has an asking price of p
The dealer knows the quality of the car, but you do not
A bad car needs additional work, costing c, to make it better
The dealer decides whether or not to put a car on sale, then you decide whether or not to buy
- Let H>p>L

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
The Market for Lemons
Nature decides whether Dealer has a good car (q) or bad car (1−q)
Note your information set:
- You are unable to determine if a Dealer choosing to Offer a good or bad car
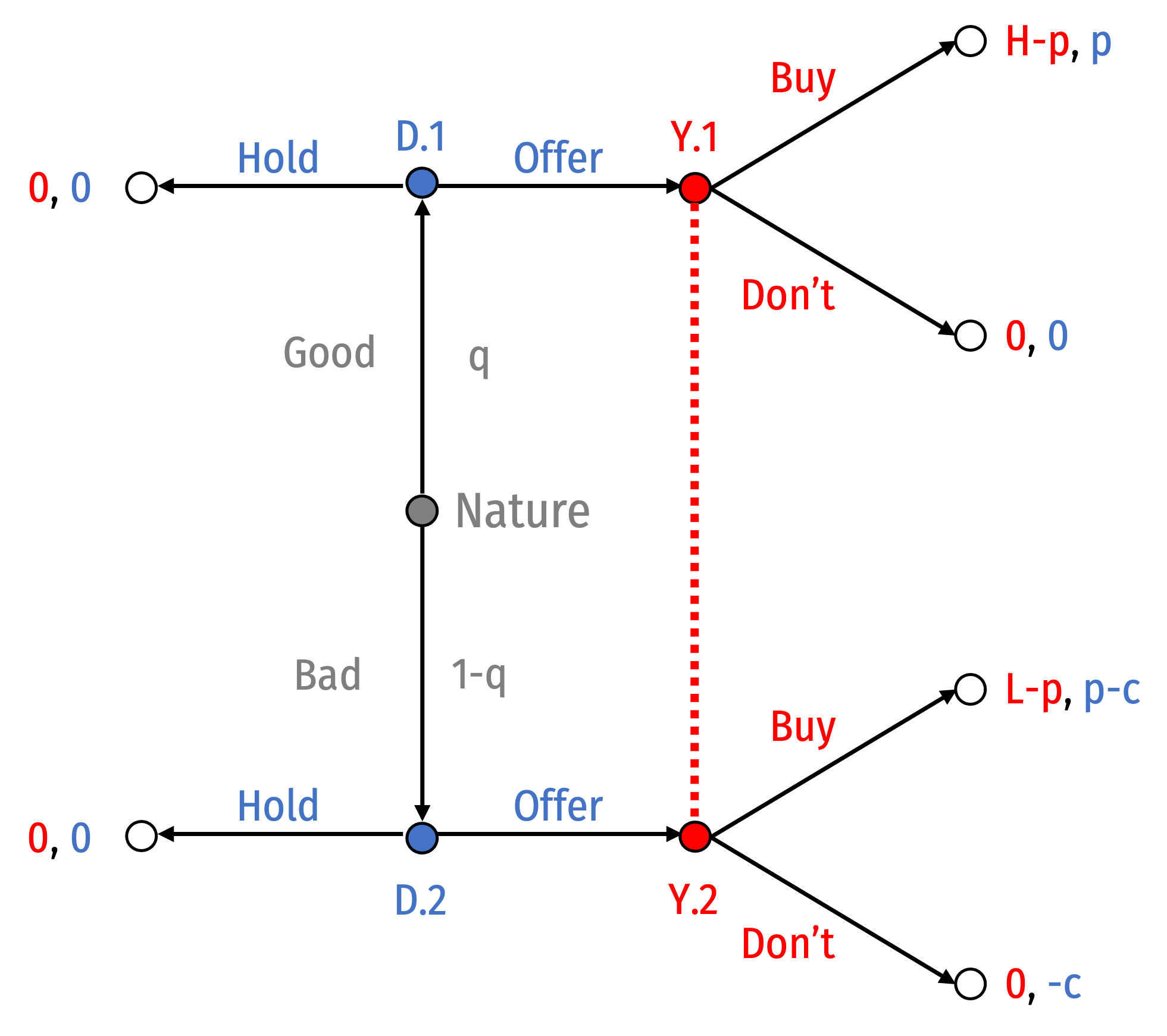
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
The Market for Lemons
Now let’s search for Perfect Bayesian Nash equilibria (PBNE)
Solve for conditions under which the following could be PBNE:
- Pooling eq. I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- Pooling eq. II: Both Types of Dealer Hold
- Separating eq. I: Good: Offer and Bad: Don't
- Separating eq. II: Good: Don't and Bad: Hold

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
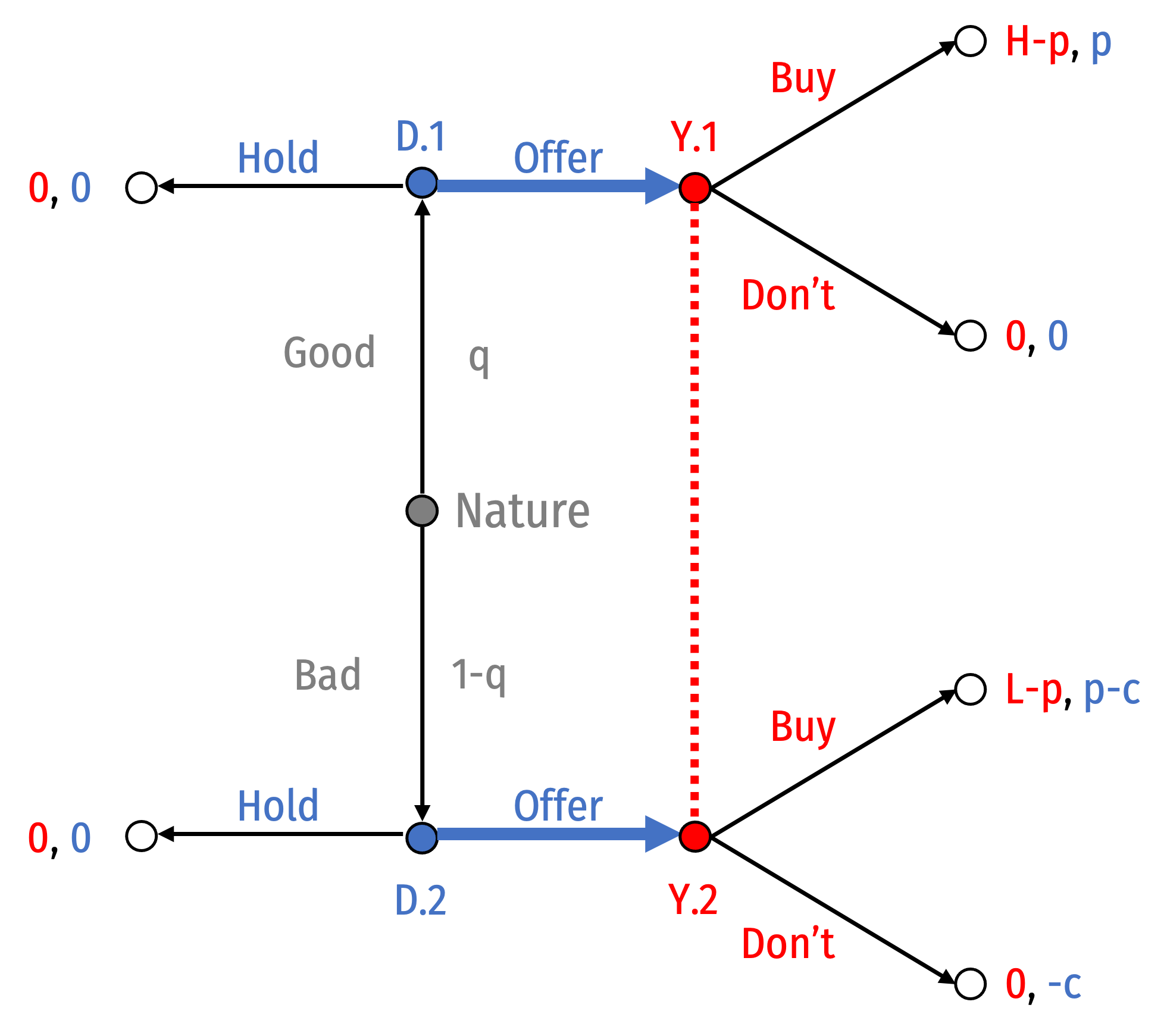
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- Suppose both types of Dealer offer
- Bayes' Rule implies:
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- Suppose both types of Dealer offer
- Bayes' Rule implies:
P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer)

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- Suppose both types of Dealer offer
- Bayes' Rule implies:
P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer)P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer|good)P(good)+P(offer|bad)P(bad)

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- Suppose both types of Dealer offer
- Bayes' Rule implies:
P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer)P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer|good)P(good)+P(offer|bad)P(bad)P(good|offer)=1×q1×q+1(1−q)

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- Suppose both types of Dealer offer
- Bayes' Rule implies:
P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer)P(good|offer)=P(offer|good)P(good)P(offer|good)P(good)+P(offer|bad)P(bad)P(good|offer)=1×q1×q+1(1−q)P(good|offer)=q
- Since both dealers offer, so the probability that an offer is good is q!

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
Suppose both types of Dealer offer
The probability that an offer is good is q
If you buy a car based on your beliefs, your expected payoff is:
E[Buy]=q(H−p)+(1−q)(L−p)

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
Suppose both types of Dealer offer
The probability that an offer is good is q
If you buy a car based on your beliefs, your expected payoff is:
E[Buy]=q(H−p)+(1−q)(L−p)
- Sequential rationality for You: Buy if E[Buy]>0
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
Suppose both types of Dealer offer
The probability that an offer is good is q
If you buy a car based on your beliefs, your expected payoff is:
E[Buy]=q(H−p)+(1−q)(L−p)
Sequential rationality for You: Buy if E[Buy]>0
Sequential rationality for Dealer: Offer if p>c

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Scenario I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
Suppose both types of Dealer offer
If p>c and E[Buy]>0, the following is a PBNE:
- Behavioral strategy: {Buy, (Good: Offer, Bad: Offer)}
- Belief system: P(good|offer)=q

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
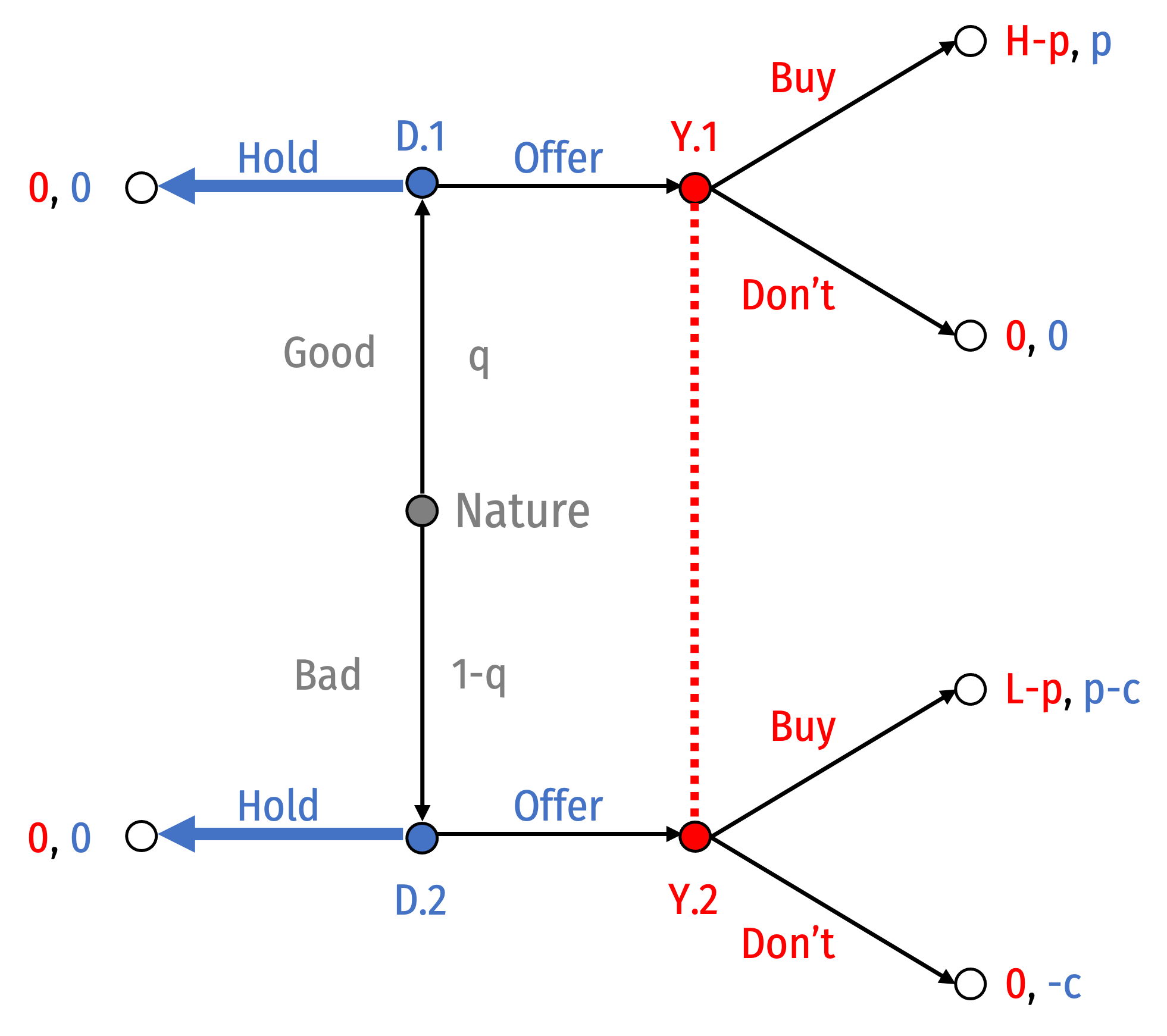
Pooling Equilibrium II: Both Types of Dealer Hold
- Suppose both types of Dealer hold
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Equilibrium II: Both Types of Dealer Hold
Suppose both types of Dealer hold
For this to be sequentially rational, You must always Not Buy
- Otherwise, Good Dealer would want to Offer
Under what beliefs would you choose Don’t? Your information set is never reached, so
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Equilibrium II: Both Types of Dealer Hold
Suppose both types of Dealer hold
For this to be sequentially rational, You must always Not Buy
- Otherwise, Good Dealer would want to Offer
Under what beliefs would you choose Don’t? Your information set is never reached, so p(Good|Offer)=0

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Pooling Equilibrium II: Both Types of Dealer Hold
Suppose both types of Dealer hold
The following is a PBNE:
- Behavioral strategy: {Don't, (Good: Hold, Bad: Hold)}
- Belief system: P(good|offer)=0
A market failure: the market unravels because of a few lemons

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
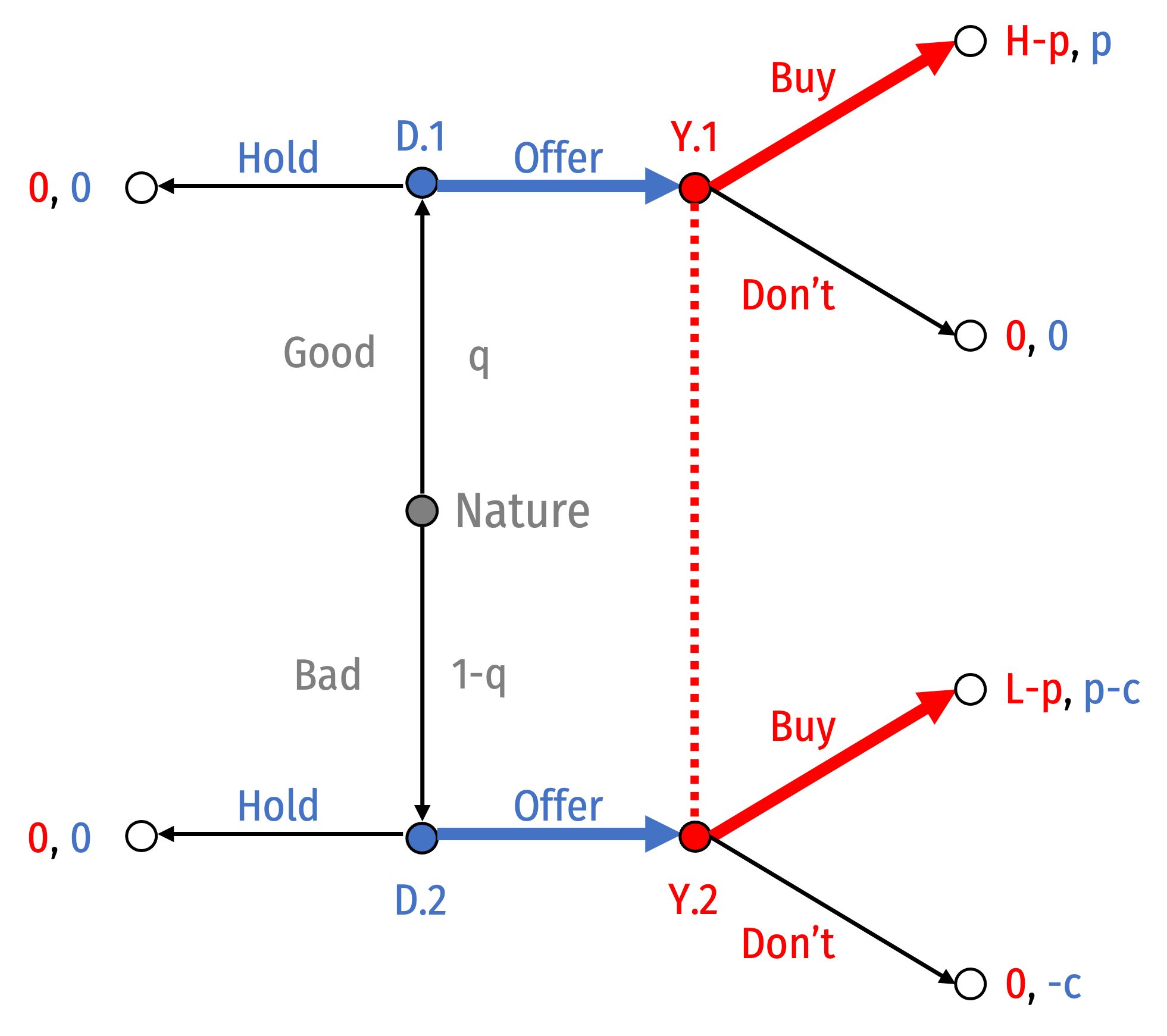
Separating Equilibrium I: Good: Offer; Bad: Hold
- Suppose Good Dealers offer and Bad Dealers hold
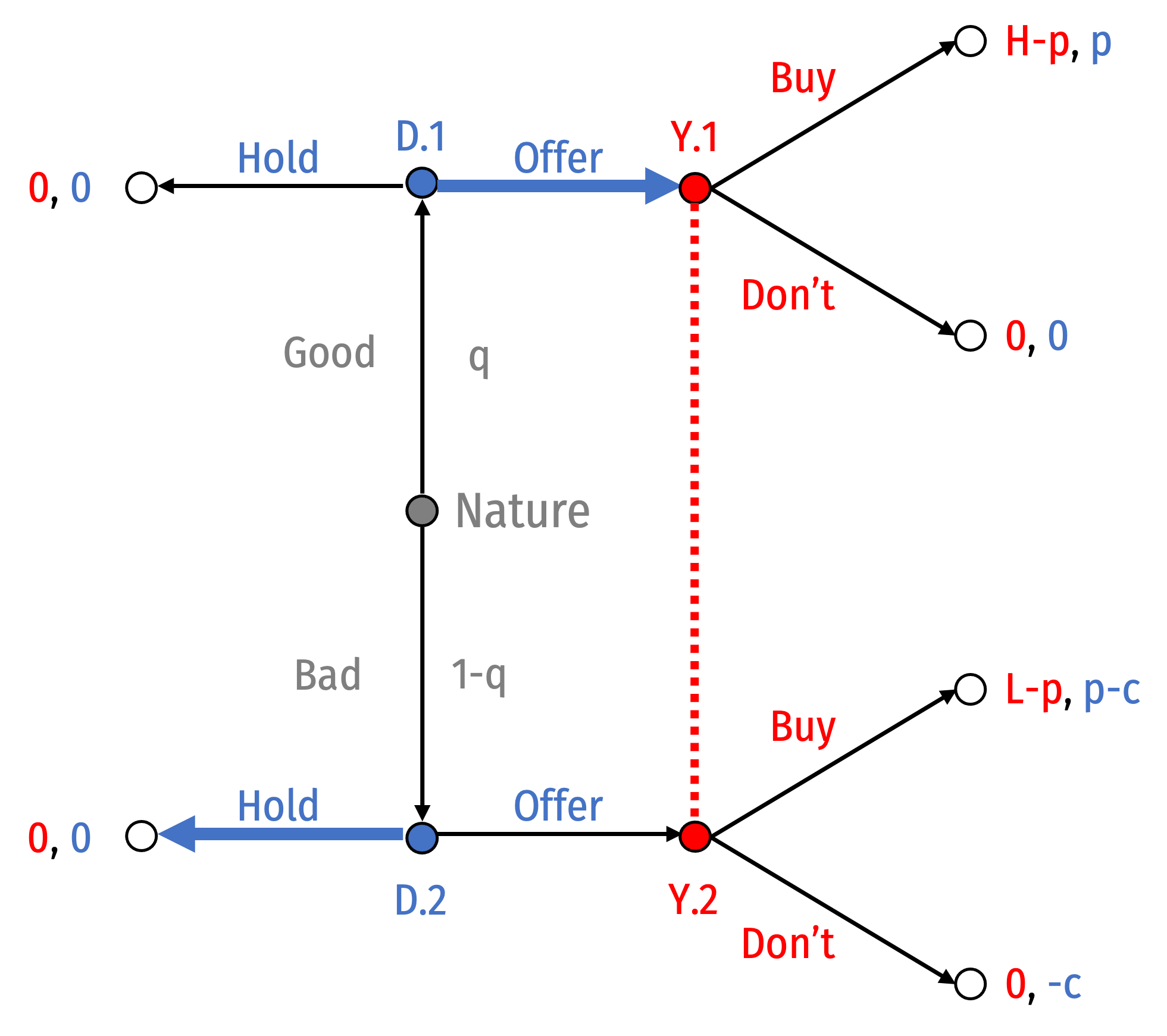
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium I: Good: Offer; Bad: Hold
Suppose Good Dealers offer and Bad Dealers hold
Bayes’ Law would imply your beliefs must be: P(Good|Offer)=1

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium I: Good: Offer; Bad: Hold
Suppose Good Dealers offer and Bad Dealers hold
Bayes’ Law would imply your beliefs must be: P(Good|Offer)=1
You buy if any type of Dealer offers
Good Dealer wants to Offer since You will Buy
Bad Dealer will Hold if p<c
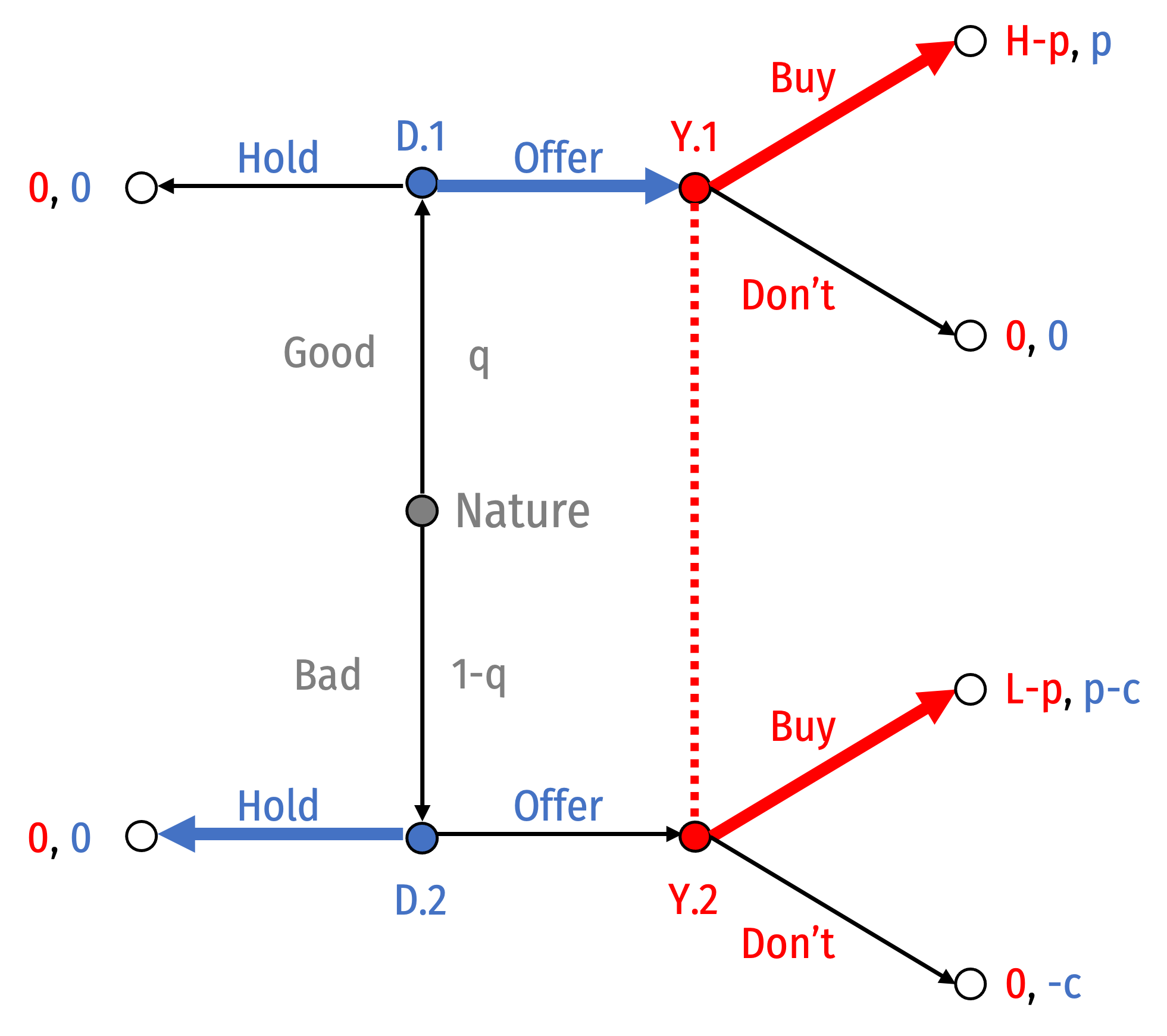
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium I: Good: Offer; Bad: Hold
Suppose Good Dealers offer and Bad Dealers hold
The following is a PBNE:
- Behavioral strategy: {Buy, (Good: Offer, Bad: Hold)}
- Belief system: P(good|offer)=0
This is the important PBNE, we will return to it

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
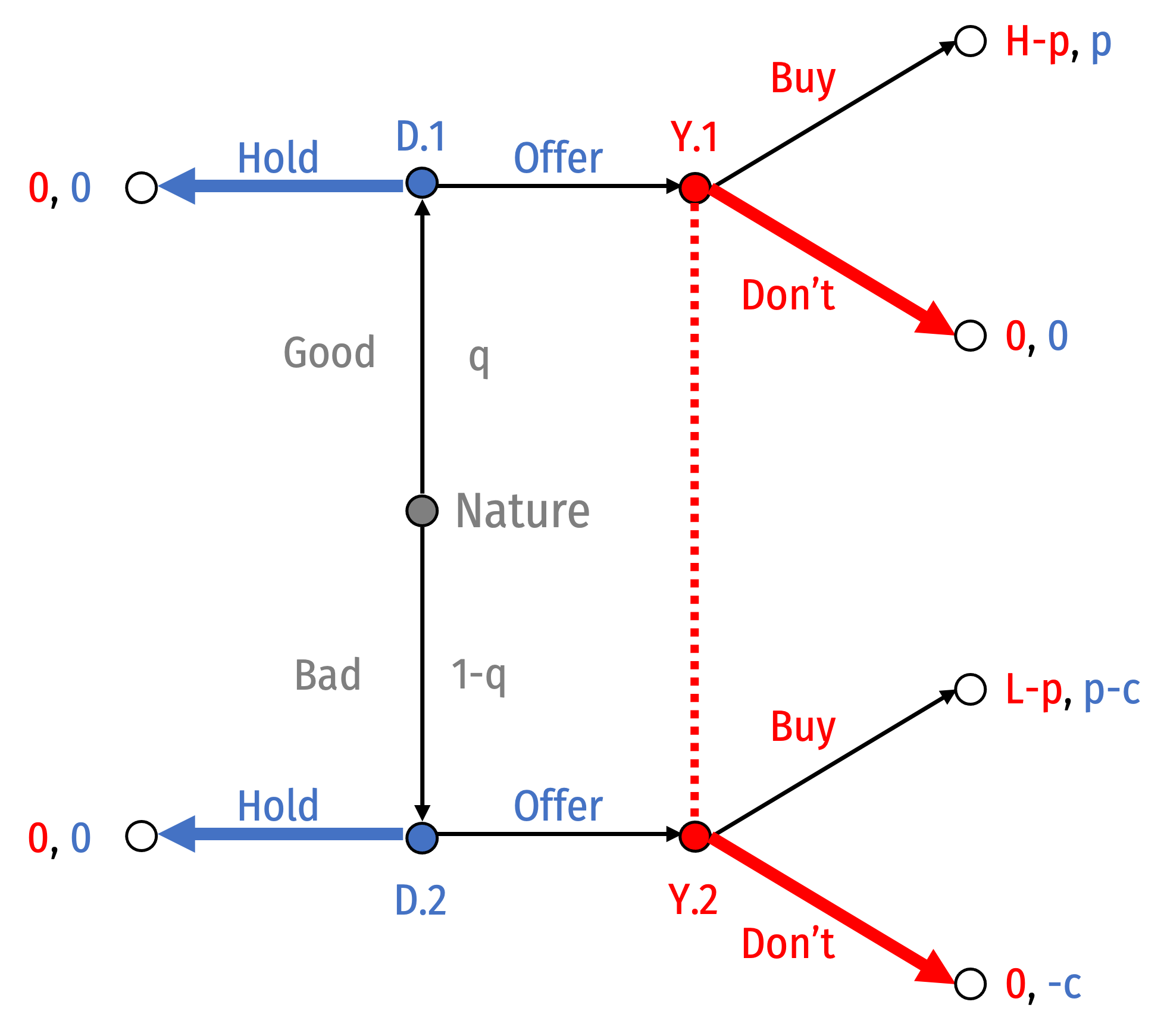
Separating Equilibrium II: Good: Hold; Bad: Offer
- Suppose Good Dealers hold and Bad Dealers offer
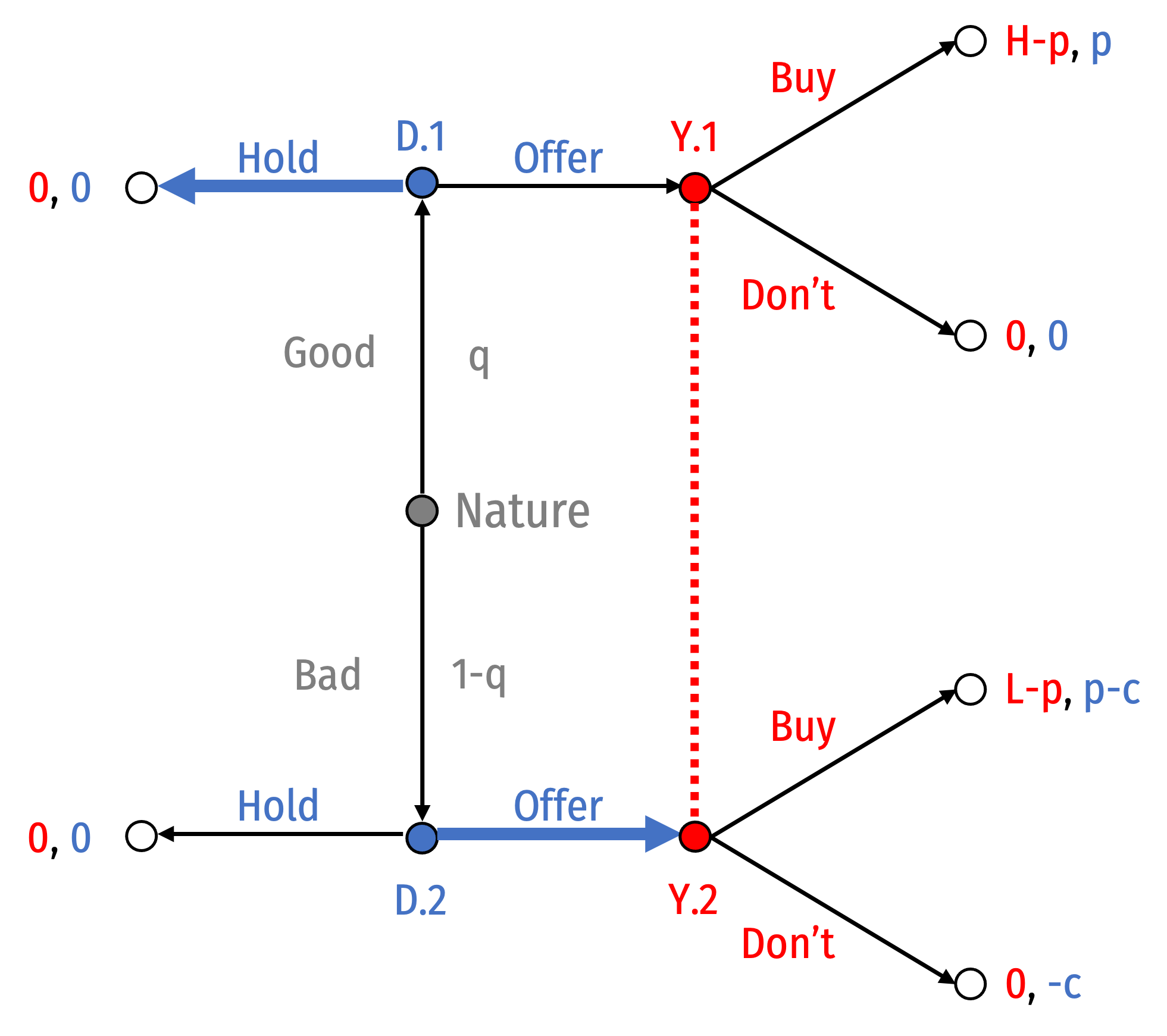
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium II: Good: Hold; Bad: Offer
Suppose Good Dealers hold and Bad Dealers offer
Bayes’ Law would imply your beliefs: P(Good|Offer)=0

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium II: Good: Hold; Bad: Offer
Suppose Good Dealers hold and Bad Dealers offer
Bayes’ Law would imply your beliefs: P(Good|Offer)=0
You Don't Buy if any Dealer Offers
- Good Dealer wants to Hold since You Don't Buy
- Bad Dealer would want to switch to Hold since You Don't Buy
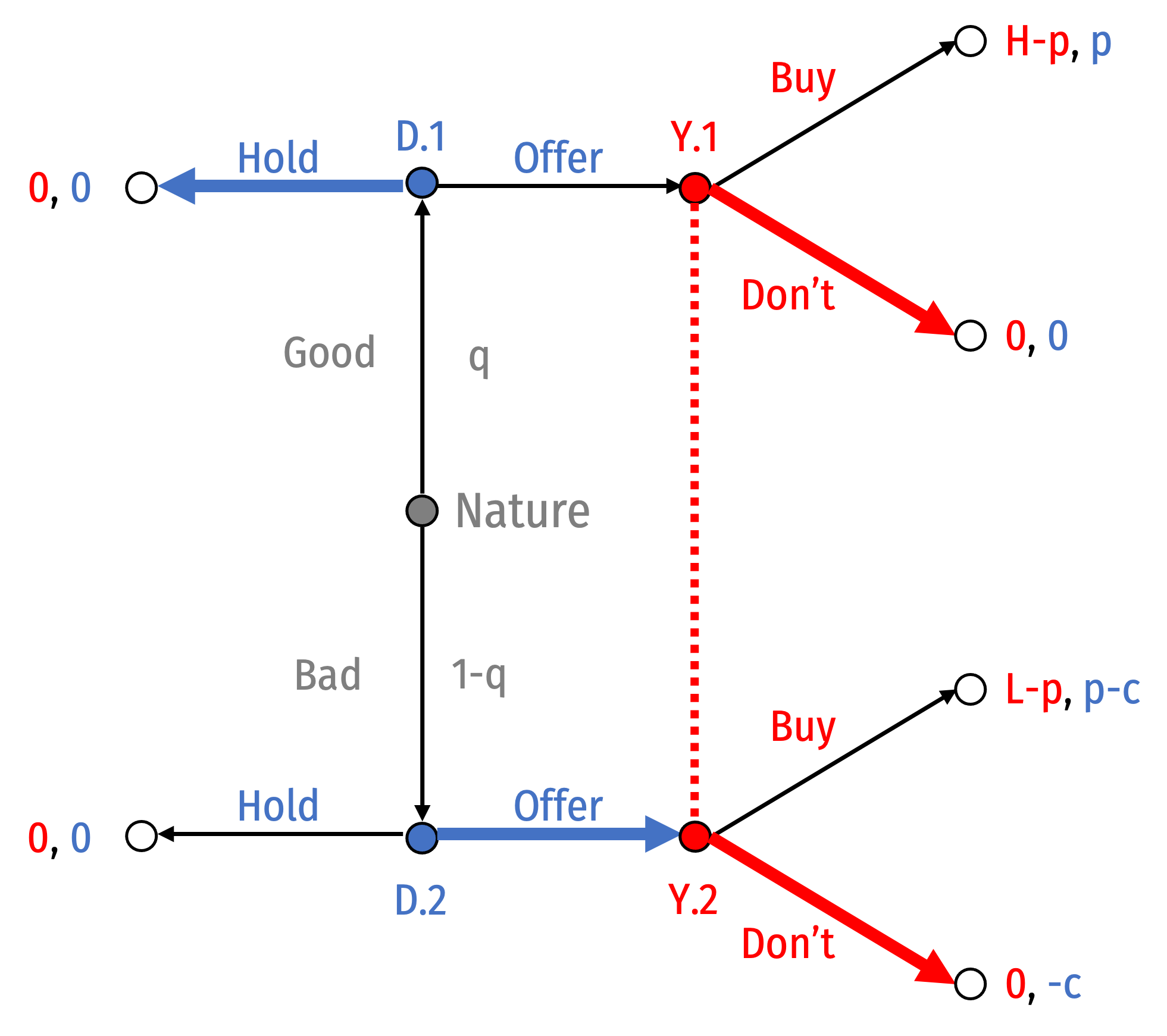
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium II: Good: Hold; Bad: Offer
Suppose Good Dealers hold and Bad Dealers offer
Bayes’ Law would imply your beliefs: P(Good|Offer)=0
You Don't Buy if any Dealer Offers
- Good Dealer wants to Hold since You Don't Buy
- Bad Dealer would want to switch to Hold since You Don't Buy
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Separating Equilibrium II: Good: Hold; Bad: Offer
Suppose Good Dealers hold and Bad Dealers offer
There is no PBNE where {(Good: Bad, Bad: Offer)}

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
The Market for Lemons
- Conditions under which the following could be PBNE:
Pooling eq. I: Both Types of Dealer Offer
- You Buy
- When p<c, E[Buy]>0, and P(Good|Offer)=1
Pooling eq. II: Both Types of Dealer Hold
- You Don't Buy
- When P(Good|Offer)=0
Separating eq. I: Good: Offer and Bad: Don't
- You Buy
- When c>p, P(Good|Offer)=1
Separating eq. II: Good: Don't and Bad: Hold
- Impossible

Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
The Market for Lemons
The desirable separating equilibrium (Good Dealers offer; Bad Dealers hold) is achieved via a costly signal
- If p<c, Dealers will only offer cars if they are good
- Too costly for a bad dealer to offer a car
In real life markets:
- CarFax
- Warranties


Market-Solutions to Asymmetric Info

George Akerlof
1940—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Numerous institutions arise to counteract the effects of quality uncertainty. One obvious institution is guarantees. Most consumer durables carry guarantees to ensure the buyer of some normal expected quality. One natural result of our model is that the risk is borne by the seller rather than by the buyer,” (p. 499).
“A second example of an institution which counteracts the effects of quality uncertainty is the brand-name good. Brand names not only indicate quality but also give the consumer a means of retaliation if the quality does not meet expectations,” (pp.499-500).
Market-Solutions to Asymmetric Info

George Akerlof
1940—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Chains - such as hotel chains or restaurant chains - are similar to brand names, (p.500)
“Licensing practices also reduce quality uncertainty,” (p.500).
Akerlof, George A, 1970, “The Market for 'Lemons': Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism,” Quarterly Journal of Economics 84(3): 488-500
Signaling Example II: Spence (1973) Job-Market Signaling
The Economics of Higher Education
Workers with more education earn higher wages, the question is why:
Human capital theory
- on the margin, higher education increases workers' productivity
- workers with more education become more productive
- workers weigh MB and MC of buying additional amounts of education

The Economics of Higher Education
Workers with more education earn higher wages, the question is why:
Signaling theory
- on the margin, higher education does not increase workers' productivity
- obtaining higher education signals (pre-existing) ability
- only workers with already-high ability get higher education

Job Market Signalling

A. Michael Spence
1943—
Economics Nobel 2001
“To hire someone, then, is frequently to purchase a lottery. In what follows, I shall assume the employer pays the certain monetary equivalent of the lottery to the individual as wage. If he is risk-neutral, the wage is taken to be the individual's marginal contribution to the hiring organization.
Spence, A Michael, 1973, “Job Market Signaling” Quarterly Journal of Economics 87(3): 355-374
Job Market Signalling

A. Michael Spence
1943—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Primary interest attaches to how the employer perceives the lottery, for it is these perceptions that determine the wages he offers to pay. We have stipulated that the employer cannot directly observe the marginal product prior to hiring. What he does observe is a plethora of personal data in the form of observable characteristics and attributes of the individual, and it is these that must ultimately determine his assessment of the lottery he is buying. (The image that the individual presents includes education, previous work, race, sex, criminal and service records, and a host of other data.) This essay is about the endogenous market process whereby the employer requires (and the individual transmits) information about the potential employee, which ultimately determines the implicit lottery involved in hiring, the offered wages, and in the end the allocation of jobs to people and people to jobs in the market,” (pp.356-357).
Spence, A Michael, 1973, “Job Market Signaling” Quarterly Journal of Economics 87(3): 355-374
Job Market Signalling

A. Michael Spence
1943—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Of those observable, personal attributes that collectively constitute the image the job applicant presents, some are immutably fixed, while others are alterable. For example, education is something that the individual can invest in at some cost in terms of time and money. On the other hand, race and sex are not generally thought to be alterable. I shall refer to observable, unalterable attributes as indices, reserving the term signals for those observable characteristics attached to the individual that are subject to maniplllation by him. Some attributes, like age, do change, but not at the discretion of the individual. In my terms, these are indices,” (pp.357).
Job Market Signalling

A. Michael Spence
1943—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Signals, on the other hand, are alterable and therefore potentially subject to manipulation by the job applicant. Of course, there may be costs of making these adjustments. Education, for example, is costly. We refer to these costs as signaling costs. Notice that the individual, in acquiring an education, need not think of himself as signaling. He will invest in education if there is sufficient return as defined by the offered wage sched~le.I~ndividuals, then, are assumed to select signals (for the most part, I shall talk in terms of education) so as to maximize the difference between offered wages and signaling costs,” (357).
Spence, A Michael, 1973, “Job Market Signaling” Quarterly Journal of Economics 87(3): 355-374
Spence’s Model
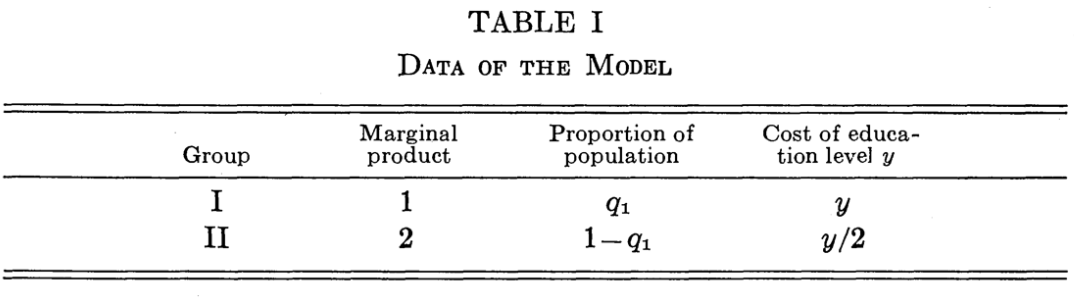
A very simple numerical example
Two groups I (low-ability) and II (high-ability) with different marginal products that firms cannot directly observe
- Group I is q1 fraction of population
Each can choose to get y amount of education which costs y to Group I, y2 to Group II
Spence’s Model
Assume labor markets are competitive
- A worker's wage is equal to their expected output
If employers could know a worker’s ability:
- Wages would then be:
- 1 for Group I (low ability)
- 2 for Group II (high ability)
In this scenario, nobody gets any education!
- Best outcome for high ability workers (Group II)

Spence’s Model
If employers cannot determine a worker’s ability:
Firm would have to offer expected marginal product to all workers:
E[W]=1(q1)+2(1−q1)E[W]=2−q1

Spence’s Model
If firms could (only) observe a worker's education level:
- Wages only depend on level of education
To offer a wage, firms must form beliefs about workers’ ability (given their education level)

Spence’s Model
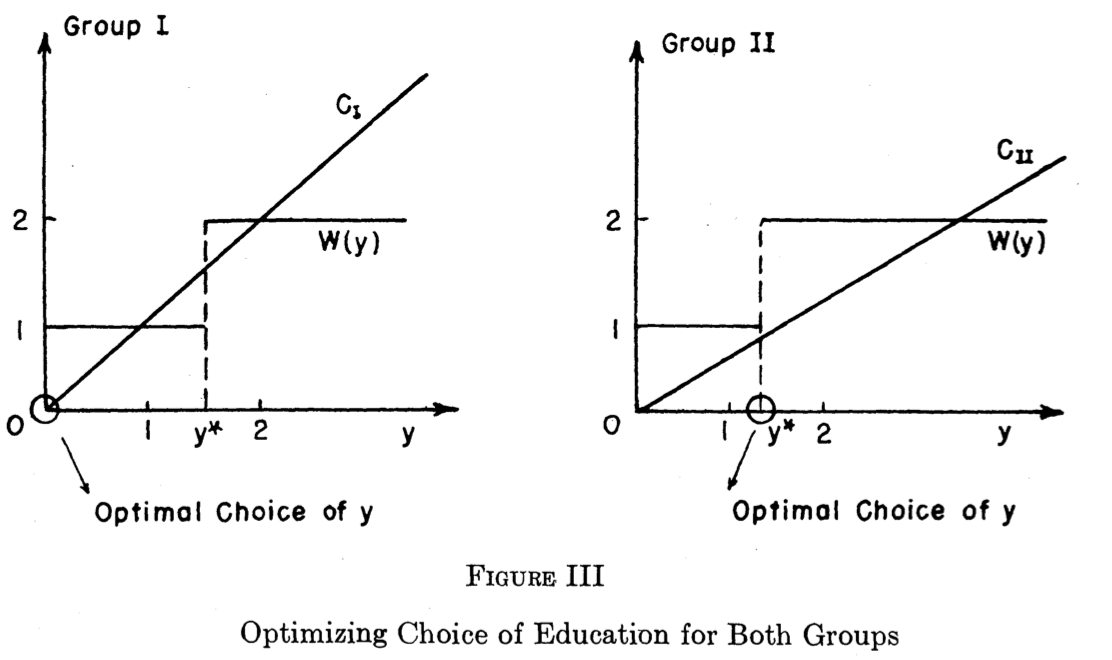
- Suppose firms believe there is some amount of education y⋆ such that if:
- a worker has less than y⋆ education, they are low ability (Group I), thus firm offers them wage of 1
- a worker has at least y⋆ education, they are high ability (Group II), thus firm offers them wage of 2
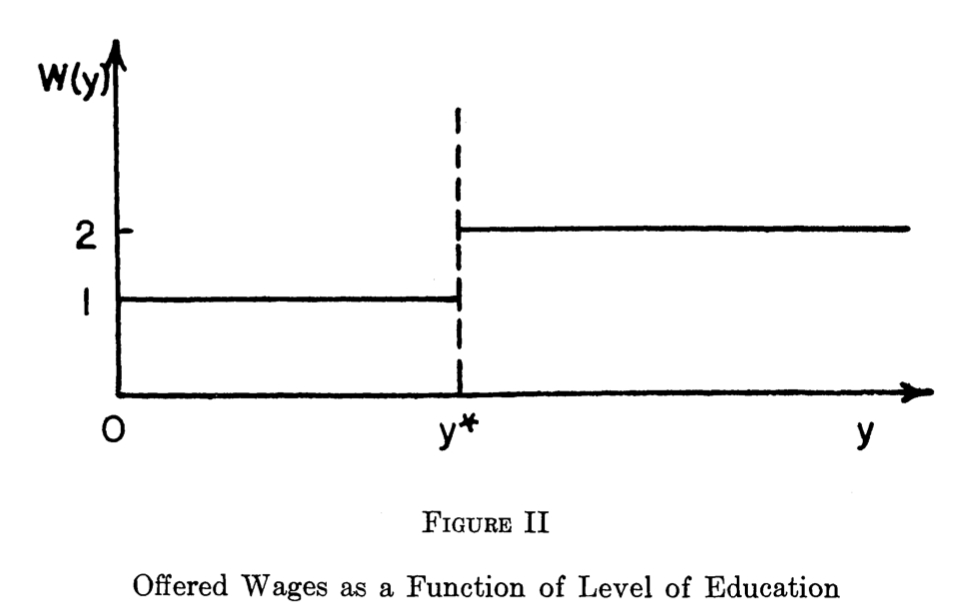
Spence’s Model
Suppose firms believe there is some amount of education y⋆ such that if:
- a worker has less than y⋆ education, they are low ability (Group I)
- a worker has at least y⋆ education, they are high ability (Group II)
Then Group I will get no education y=0 (so long as 2−y⋆<1), and Group II will get y⋆ education (so long as 2−y⋆2>1)
This signalling equilibrium occurs when 1<y∗<2
Spence’s Model

A. Michael Spence
1943—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Increases in the level of y⋆ hurt Group II, while, at the same time, members of Group I are unaffected. Group I is worse off than it was with no signaling at all. For if no signaling takes place, each person is paid his unconditional expected marginal product, which is just [2−q1]. Group II may also be worse off than it was with no signaling. Assume that the proportion of people in Group I is 0.5. Since y⋆>1 and the net return to the member of Group I1 is 2−⋆2, in equilibrium his net return must be below 1.5, the no-signaling wage. Thus, everyone would prefer a situation in which there is no signaling,” (p.364).
Spence, A Michael, 1973, “Job Market Signaling” Quarterly Journal of Economics 87(3): 355-374
Spence’s Model

A. Michael Spence
1943—
Economics Nobel 2001
“Given the signaling equilibrium, the education level y⋆, which defines the equilibrium, is an entrance requirement or prerequisite for the high-salary job - or so it would appear from the outside. From the point of view of the individual, it is a prerequisite that has its source in a signaling game. Looked at from the outside, education might appear to be productive. It is productive for the individual, but, in this example, it does not increase his real marginal product at all,” (p.364).
Spence, A Michael, 1973, “Job Market Signaling” Quarterly Journal of Economics 87(3): 355-374
Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
Suppose there are two types of workers:
- H: high ability, in proportion q
- L: low ability, in proportion 1−q
Workers output (productivity) is equal to
- H if high ability
- L if low ability

Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
Workers choose to get (high) education or no (low) education
- Low education costs nothing
- High education costs:
- cH to high ability worker
- cL to low ability worker
Education has no impact on worker's output (productivity)!

Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
Assume labor markets are competitive
- A worker's wage is equal to their expected output
If employers could know a worker’s ability:
- Wages would then be:
- wH=H for high ability
- wL=L for low ability
In this scenario, nobody gets any education!
- Best outcome for High ability workers

Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
If employers could only observe a worker's education level:
- Wages only depend on level of education
To offer a wage, employers must form beliefs about workers’ ability (given their education level)

Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
Consider the conditions for one separating equilibrium where:
- high-ability workers acquire (more) education
- low-ability workers acquire no (or less) education
Employers offer wages:
- wH=H
- wL=L
Employer beliefs:
- P(High Ability|Education)=1
- P(Low Ability|No Education)=1

Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
- High-ability workers: choose to get Education if H−cH>L
Low-ability workers: choose to get No Education if L>H−cL
Main condition: cH<H−L<cL

Essence of the Signaling Model of Education
Higher education contributes nothing to productivity, but is more costly for low ability workers
- High ability workers incur the cost of high education just to signal they are high ability
- Low ability workers cannot afford to incur the cost, and don't get high education
In signalling equilibrium, high ability workers are worse off by cH

Signaling Example III: Leeson (2012) Ordeals
Obligatory
Ordeals

Peter Leeson
1979—
“For 400 years the most sophisticated persons in Europe decided difficult criminal cases by asking the defendant to thrust his arm into a cauldron of boiling water and fish out a ring. If his arm was unharmed, he was exonerated. If not, he was convicted. Alternatively, a priest dunked the defendant in a pool. Sinking proved his innocence; floating proved his guilt. People called these trials ordeals. No one alive today believes ordeals were a good way to decide defendants’ guilt. But maybe they should...Medieval judicial ordeals achieved what they sought: a way of accurately assigning guilt and innocent where traditional means couldn’t.”
Leeson, Peter T, 2012, “Ordeals,” Journal of Law and Economics 55: 691—714
Ordeals: Why They Worked
Ordeals were only used when there was uncertainty about a person's innocence or guilt
Obvious cases were settled with evidence and witnesses

Ordeals: Why They Worked
Accused is either Innocent (with probability p) or Guilty
- Choice is a message to Priest: Undergo or Refuse an ordeal
Priest observes choice, but does not know true innocence or guilt
Must find a signal such that payoffs create a separating equilibrium where (Innocent: Undergo, Guilty: refuse)

Ordeals: The Law and Economics of Superstition
Ordeals “worked” because of iudecium Dei: God would protect the truly innocent and expose the guilty during the ordeal
- Specifically, worked because of people’s believeds in iudecium Dei
Priests didn’t actually leave it in God's hands, but cleverly leveraged people's belief in iudecium Dei

Ordeals: The Law and Economics of Superstition
If people believe in iudecium Dei
and Accused ranks payoffs:
- Truly innocent: Undergo and pass
- Truly guilty: Refuse and confess
- Truly innocent: Refuse
- Truly guilty: Undergo and fail
Then Priest’s updated beliefs are:
- p(Innocent|Undergo)=1
- p(Guilty|Refuse)=1

Ordeals: The Law and Economics of Superstition
Conditional on observing the Accused’s decision to undertake ordeal, Priest knows person is (very probably) innocent
Priest rigs the Ordeal so the accused "miraculously" passes it
Events were religious, sanctimonious, ritualized, Priest had lots of (trusted) discretion

Ordeals: The Law and Economics of Superstition
Ordeals only work for people who believe in iudicium Dei
- Reserved for the most difficult cases with no evidence or witnesses
What about “skeptics”?
- Priest had to let a proportion of those undertaking ordeal fail them (even if they were innocent!)
- Maintains an equilibrium of belief in iudicium Dei
Known non-believers (or non-Christians) were not presented with Ordeals as an option

Ordeals: The Law and Economics of Superstition
In 1215, Fourth Lateran Council rejects the legitimacy of judicial ordeals, banned priests from administering them
- Belief in iudicium Dei evaporates
- Ordeals would no longer work — requires the superstition as sorting mechanism
Today we have technology that can accurately separate innocence and guilt in very hard cases (e.g. DNA evidence)

Ordeals

Peter Leeson
1979—
“Though rooted in superstition, judicial ordeals weren’t irrational. Expecting to emerge from ordeals unscathed and exonerated, innocent persons found it cheaper to undergo ordeals than to decline them. Expecting to emerge...boiled, burned, or wet and naked and condemned, guilty persons found it cheaper to decline ordeals than to undergo them. [Priests] knew that only innocent persons would want to undergo ordeals...[and] exonerated probands whenever they could. Medieval judicial ordeals achieved what they sought: they accurately assigned guilt and innocence where traditional means couldn’t.”
Leeson, Peter T, 2012, “Ordeals,” Journal of Law and Economics 55: 691—714
The Law and Economics of Superstitution: Persistance

The Law and Economics of Superstitution: Persistance
Signaling Takeaways
Signalling in Biology
The peacock's famous tail is a quintessential example
Why do we observe traits in species that reduce fitness?
- Because they are costly signals!
Handicap Principle: reliable signals must be costly to the signaler such that it is prohibitively costly for a weaker individual
Zahavi, A, 1975, “Mate selection - a selection for a handicap,” Journal of Theoretical Biology
Grafen, A, 1990, “Biological signals as handicaps,” Journal of Theoretical Biology

Sustaining Cooperation: Signaling vs. Reputation
(Credible) signals and reputation both encourage cooperation, but via different mechanisms
Reputation is an ex post enforcement mechanism for cooperation via a threat
“If you cheat, then I will sever our existing relationship in the future and tell all my friends not to trust you”
- Folk theorem requires repeat interaction and high discount rates
- Limited to your social network, where you can spread the word

Sustaining Cooperation: Signaling vs. Reputation
Signaling is an ex ante commitment via a promise
“I, a stranger, am demonstrating to you before we establish a relationship that I am trustworthy”
A good (credible) signal:
- Must be costly, not free
- But more costly for “bad” type than “good” type
A bad (non-credible) signal:
- May be free
- Or may have same cost for all types

Sustaining Cooperation: Signaling vs. Reputation


Sustaining Cooperation: Signaling vs. Reputation

Venetian trader Marco Polo in Yuan Dynasty dress
