Please read the instructions for completing homeworks.
Concepts
Question 1
Define Nash Equilibrium, and describe three separate methods that we can use to find a Nash equilibrium in simultaneous games.
Problems
Question 5
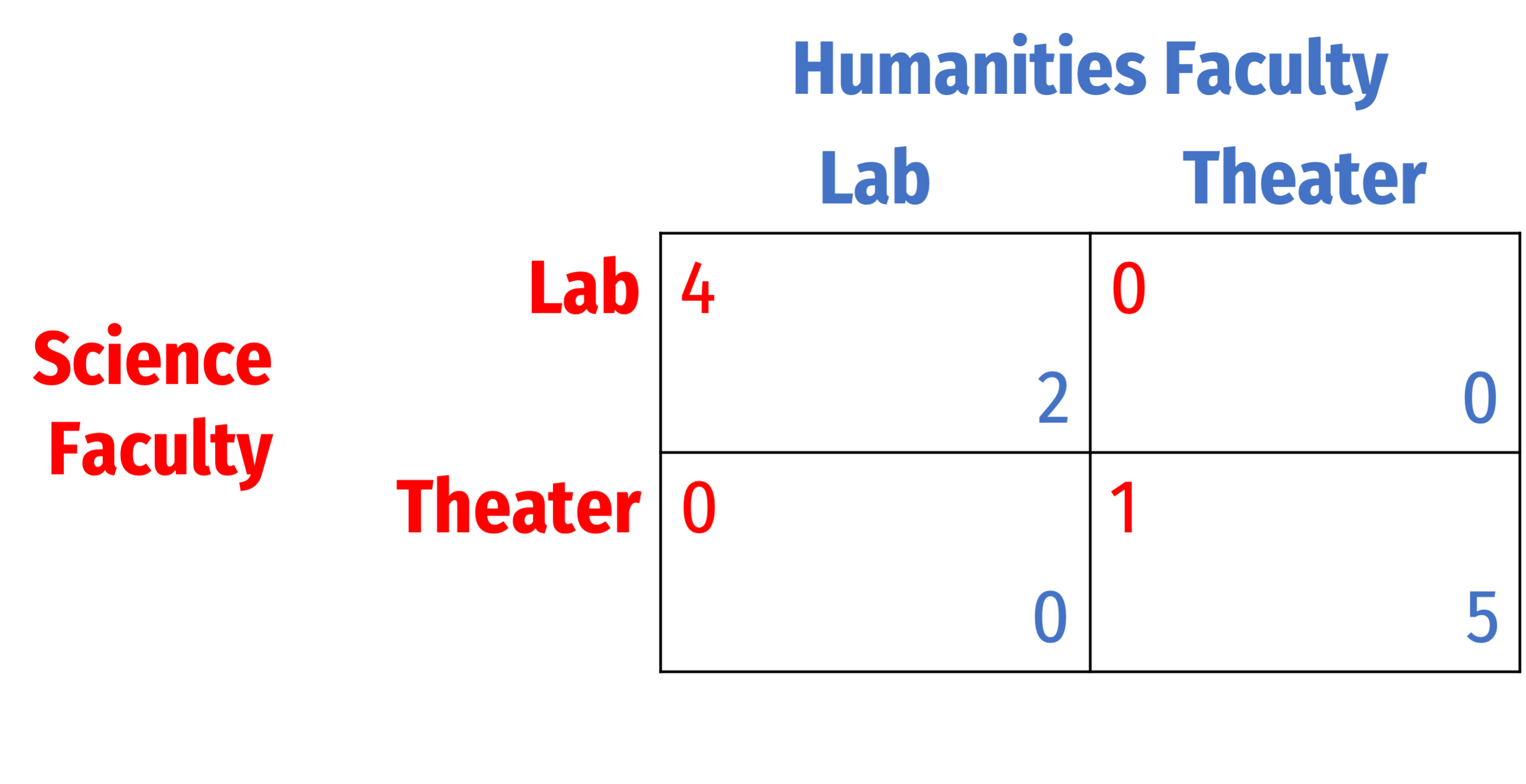
A university is contemplating whether to build a new lab or a new theater on campus. The science faculty would rather see a new lab built, and the humanities faculty would prefer a new theater. However, the funding for the project (whichever it may turn out to be) is contingent on unanimous support from the faculty. If there is disagreement, neither project will go forward, leaving each group with no new building and their worst payoff. The meetings of the two separate faculty groups on which proposal to support occur simultaneously, with payoffs given in the following table:
Question 6
Suppose it’s the early 2000’s and two Hollywood studios — Sony Pictures and Paramount Pictures — are each holding separate board meetings to strategize on how to keep up with the latest video technology. Two new advanced DVD standards are emerging on the market, HD-DVD and Blu Ray. Both firms would like to adopt a standard such that all other firms are using the same standard.
Part A
Suppose there is no clear standard emerging yet, and no firms have any strong preferences. What type of game is this? Draw the payoff matrix and find all Nash equilibria.
Part B
Suppose both firms hear rumors that another top film studio, Warner Brothers, has already committed to distributing its movies on HD-DVDs. If Sony and Paramount again must simultaneously choose a standard, what type of game is thus? Draw the new payoff matrix and find all Nash equilibria.
Part C
Suppose instead that Sony’s parent company actually has a stake in the company that produces Blue Rays. Additionally, Paramount’s board are informed that their marketing department has already told all of Paramount’s buyers that they have adopted HD-DVD, and reversing would be too embarassing. What type of game is thus? Draw the new payoff matrix and find all Nash equilibria.
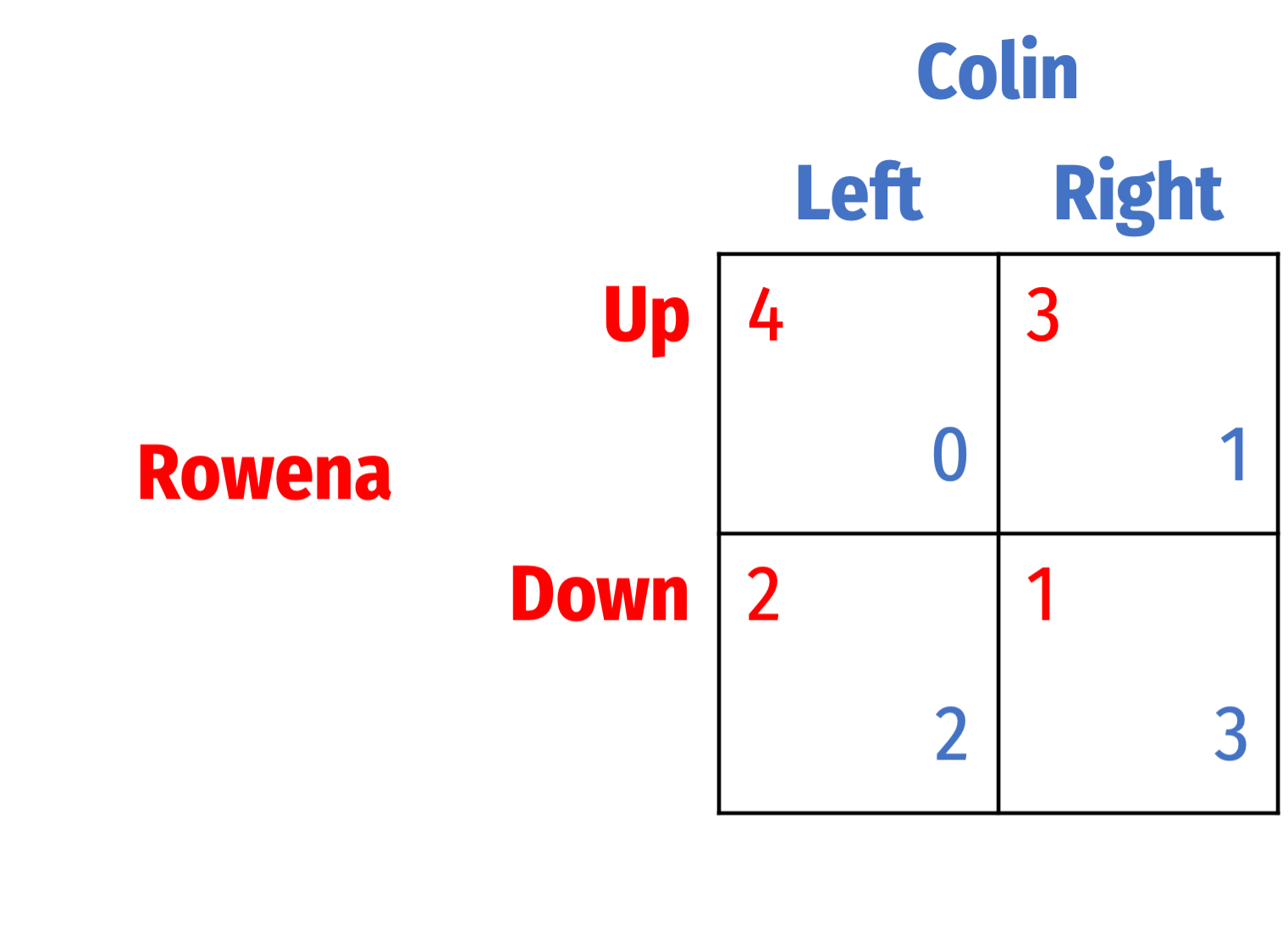
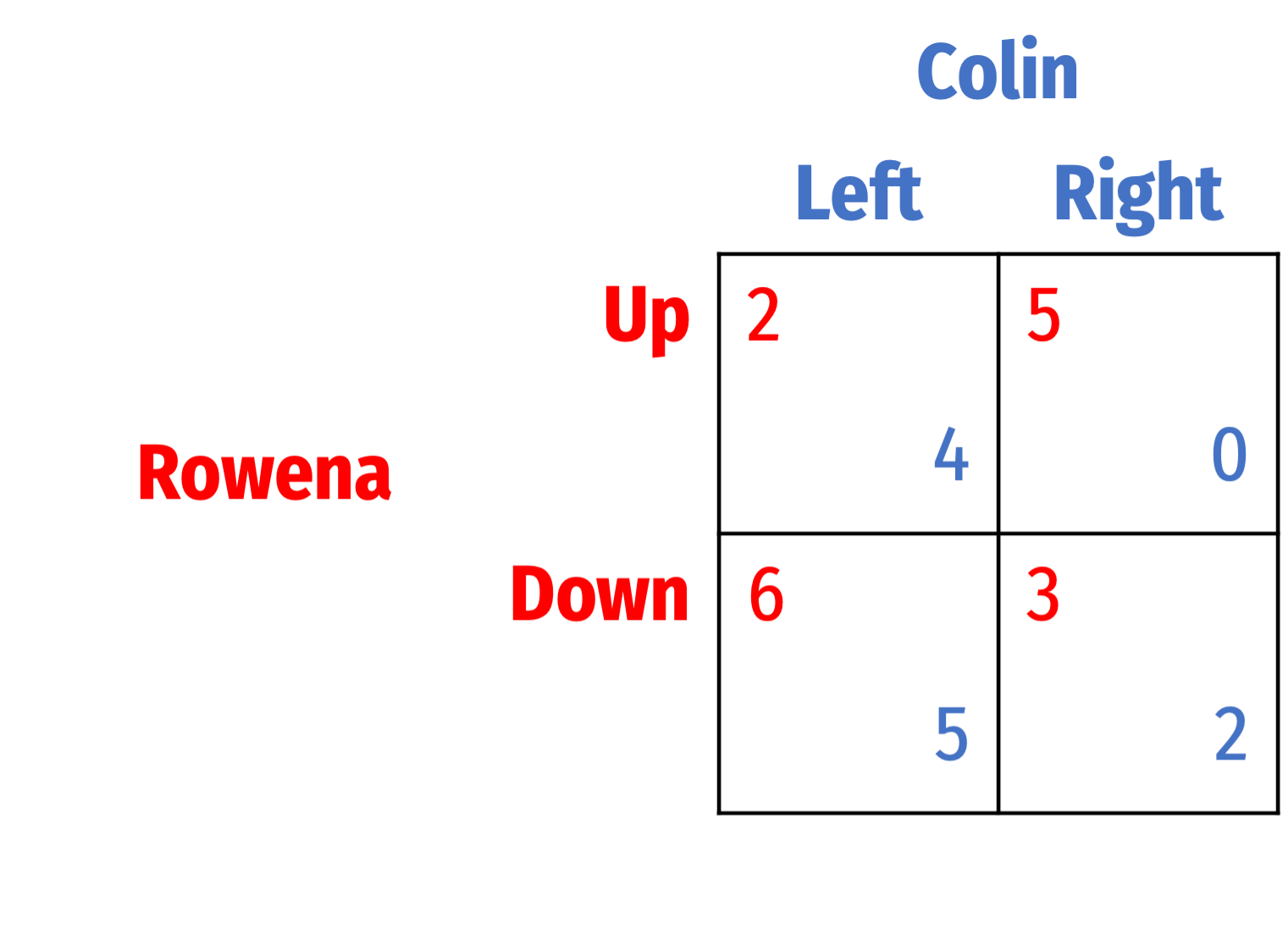
Question 7
Management and labor for a major transportation company are renegotiating their collective bargaining agreement before the crucial holiday travel season. Both labor and management will benefit from reaching any agreement, and would both suffer if no deal is reached and the company goes out of business. Each party certaintly wants to gain the most concessions from the other. Each can bargain Hard and obtain maximal concessions from the other party, or bargain Soft and ask for minimal concessions. If both bargain Hard, it is impossible for them to reach a deal.
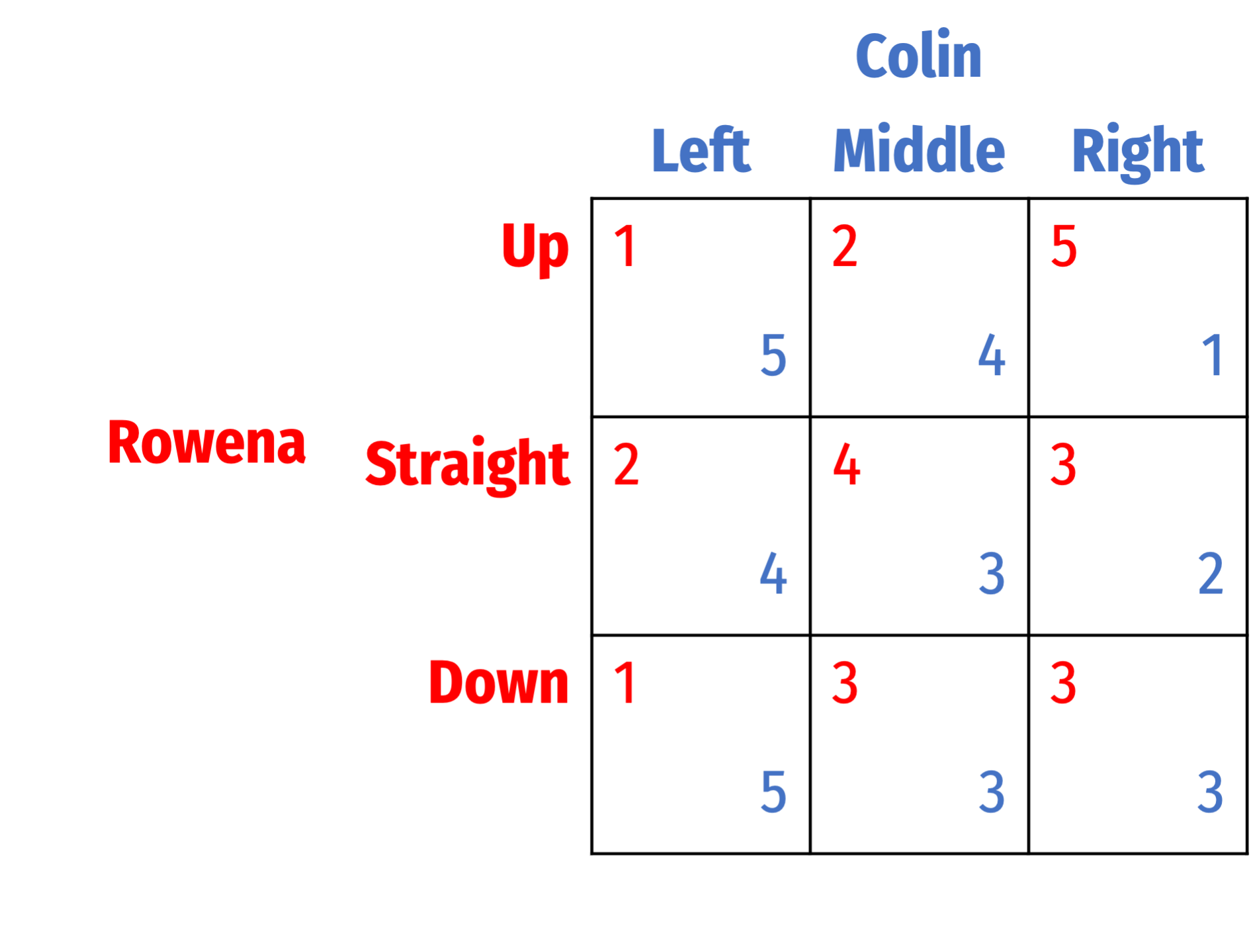
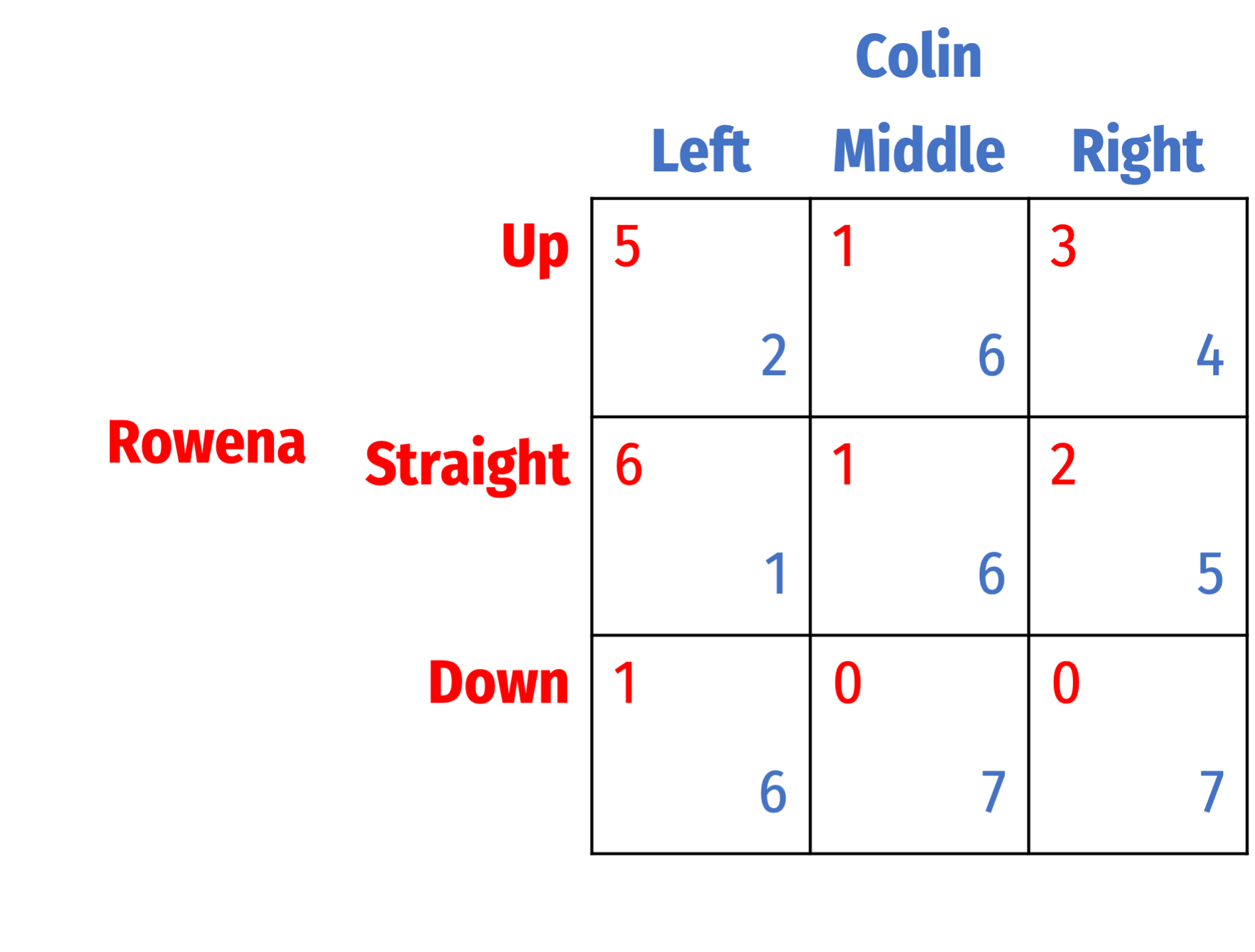
Question 8
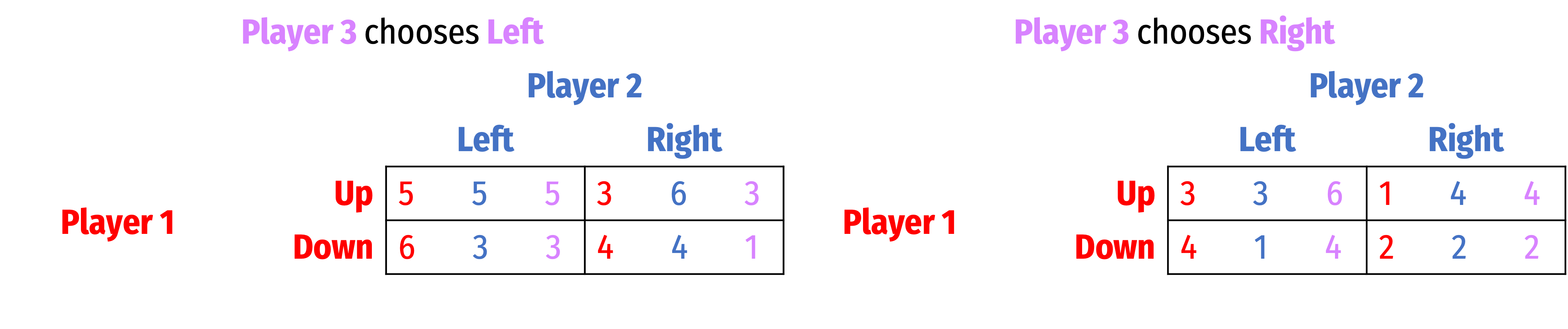
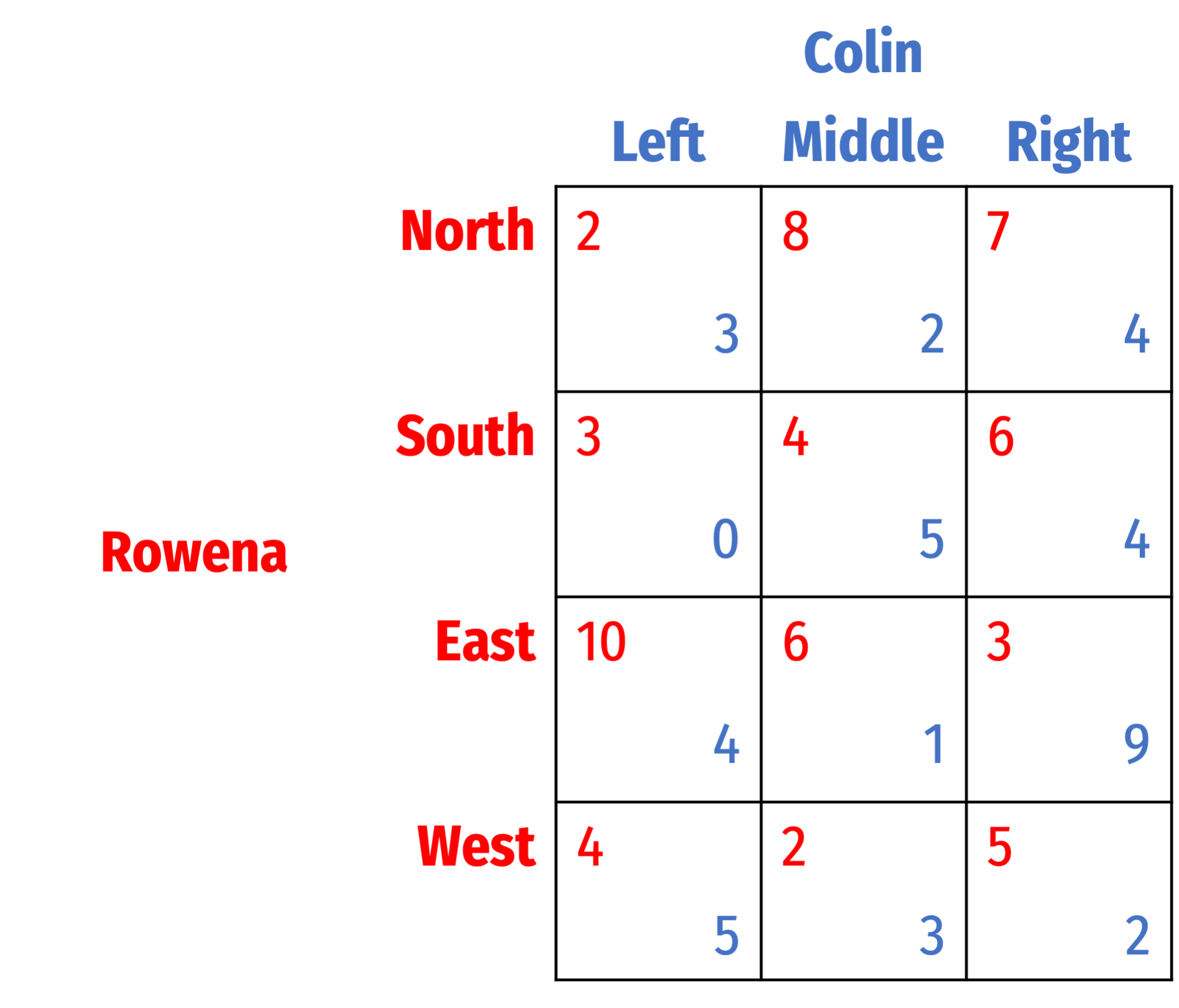
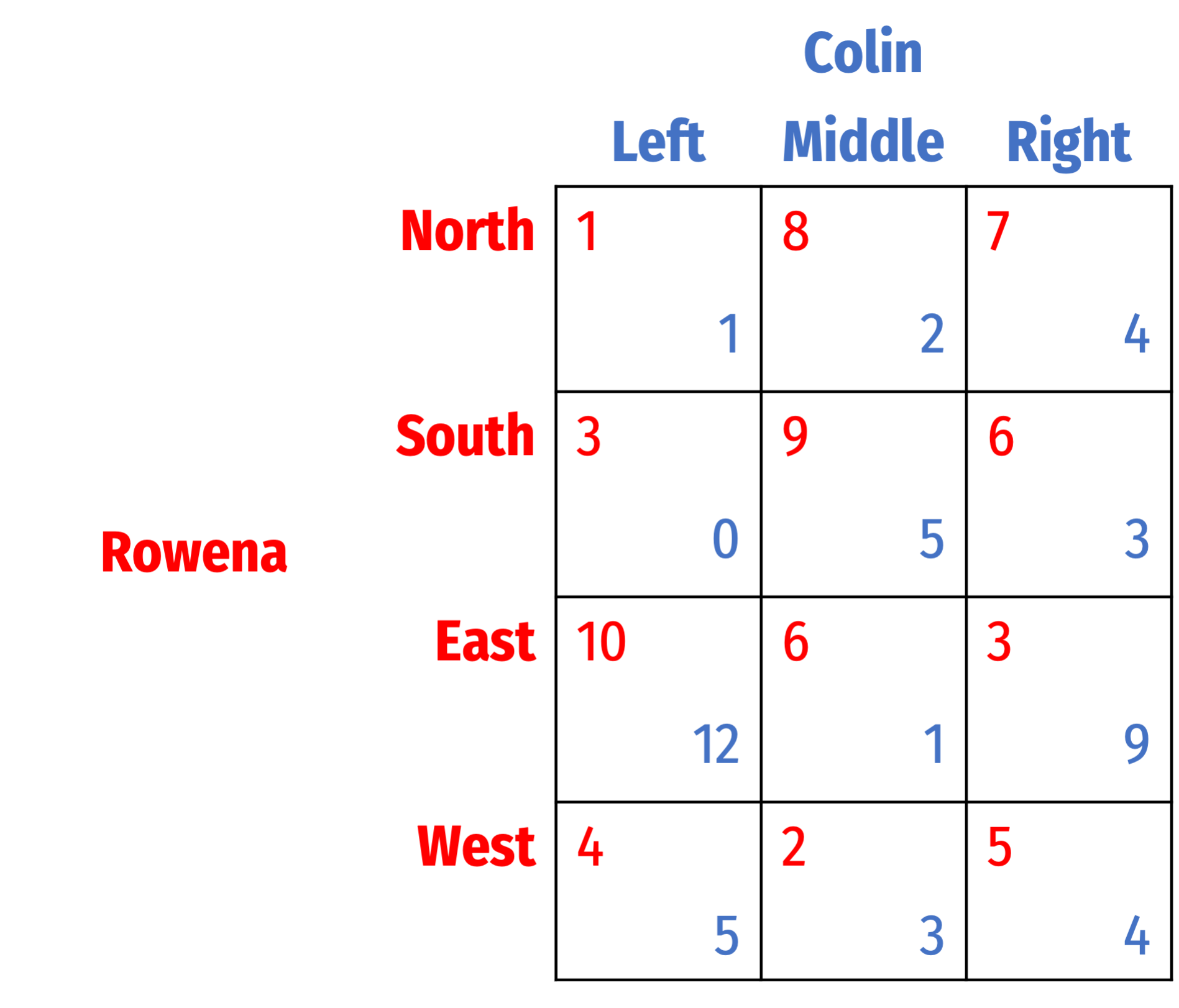
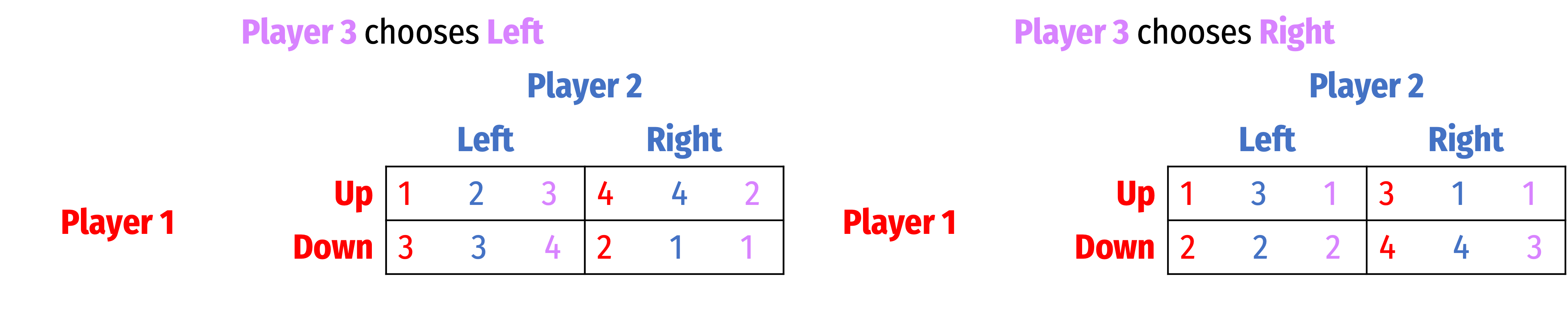
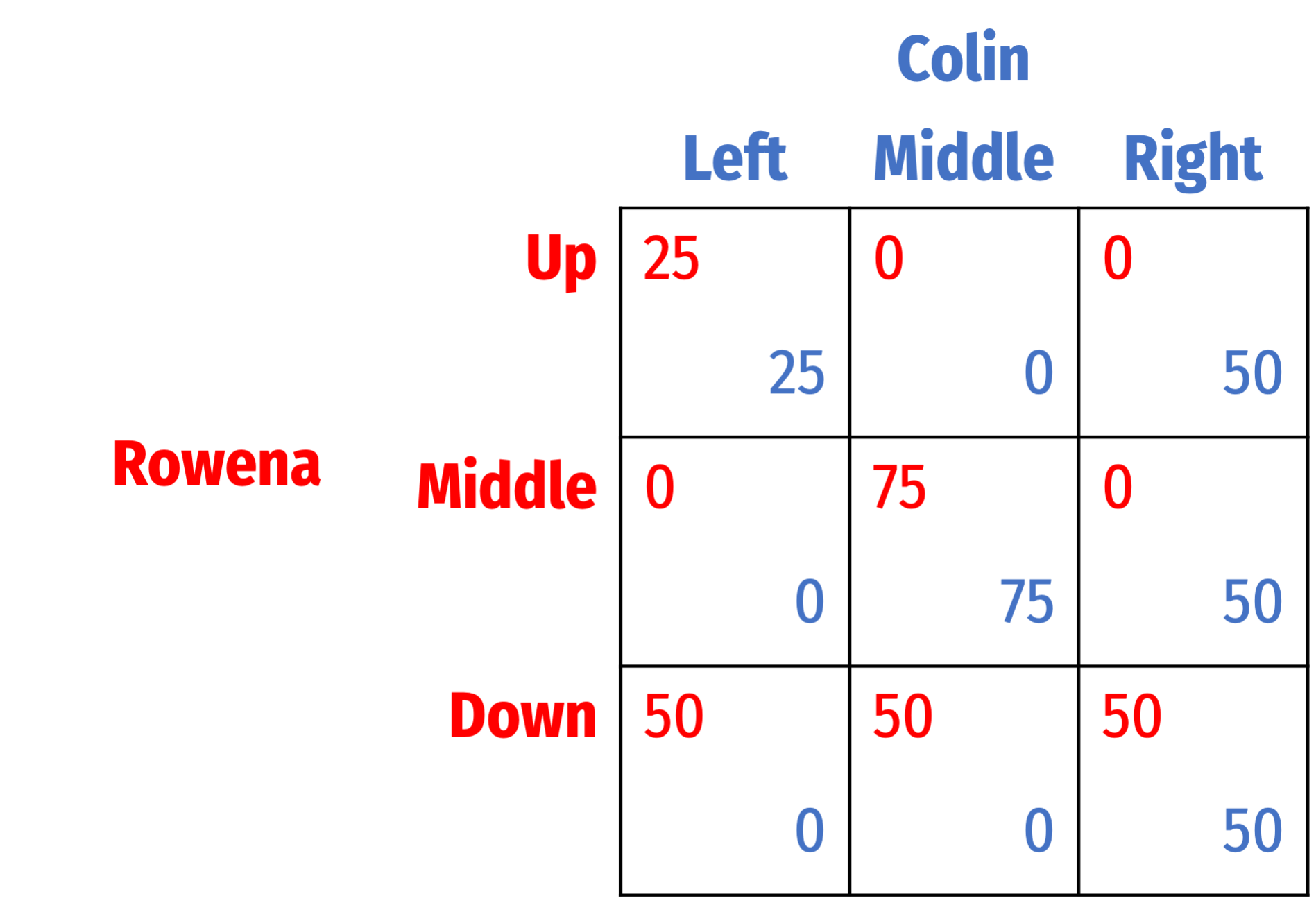
Find all Nash equilibria for the following games. First, check for dominant strategies. If there are none, solve using iterated elimination of dominant strategies. Describe your process (you can simply mark up the table, but describe what you are eliminating in what order, and why).